Redox Flow Battery Market Outlook:
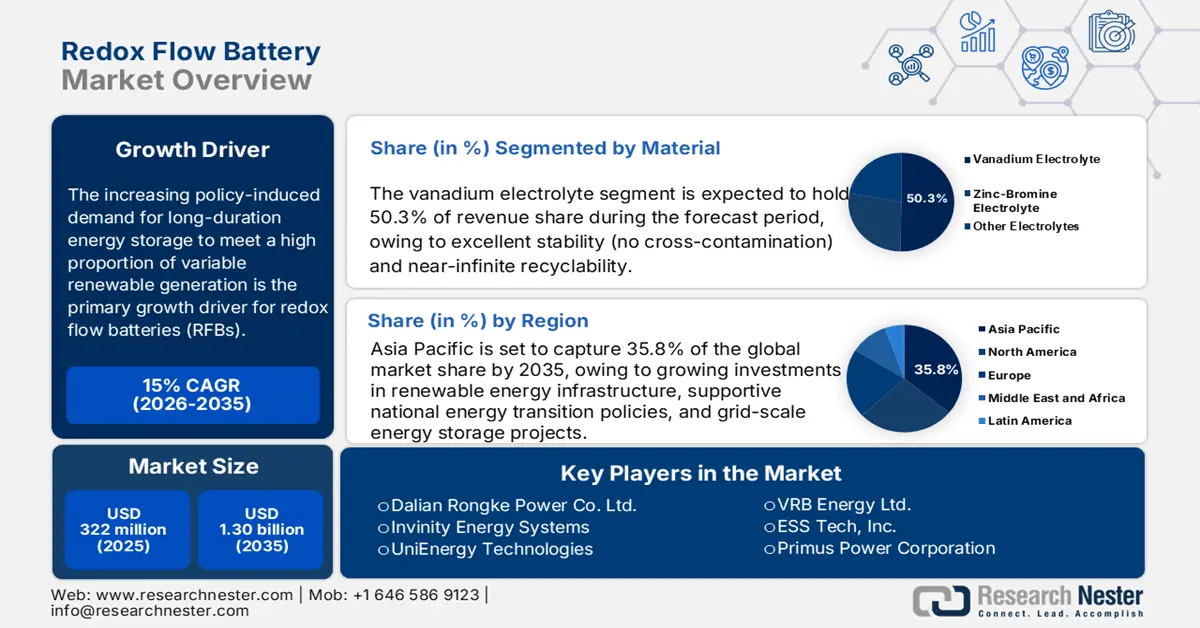
Redox Flow Battery Market size was estimated at USD 322 million in 2025 and is expected to surpass USD 1.30 billion by the end of 2035, rising at a CAGR of 15% during the forecast period, i.e., 2026-2035. In 2026, the industry size of redox flow battery is assessed at USD 370.3 million.
The increasing policy-induced demand for long-duration energy storage to meet a high proportion of variable renewable generation is the primary growth driver for redox flow batteries (RFBs). The U.S. Department of Energy states that if our grid reaches net zero by 2050, between 225 GW and 460 GW of long-duration energy storage will be required, according to a recent study. In 2021, the DOE launched its Long Duration Storage Shot initiative, committing to a 90% reduction from 2022 in 10+ hour storage technology costs, including flow batteries, by 2030 to target public R&D investment and reduce levelized storage cost by up to 60% for flow systems.
In the raw materials supply chain and manufacturing space, the availability of vanadium is a bottleneck, and it is highly concentrated production, limiting scaling to multi-gigawatt-hour deployments without significant supply growth. The price of vanadium-based systems is about $491/kWh, and iron and zinc-based systems are $196 and the lowest of $153/kWh. Both government and industry established new electrolyte production and flow battery assembly plants, for example, in South Africa, which includes vanadium beneficiation and domestic production lines for direct support to regional and export markets. The general patterns of trade are consistent for developing economies to manufacture Industry 4.0 in their region.