Nontuberculous Mycobacterium Treatment Market Outlook:
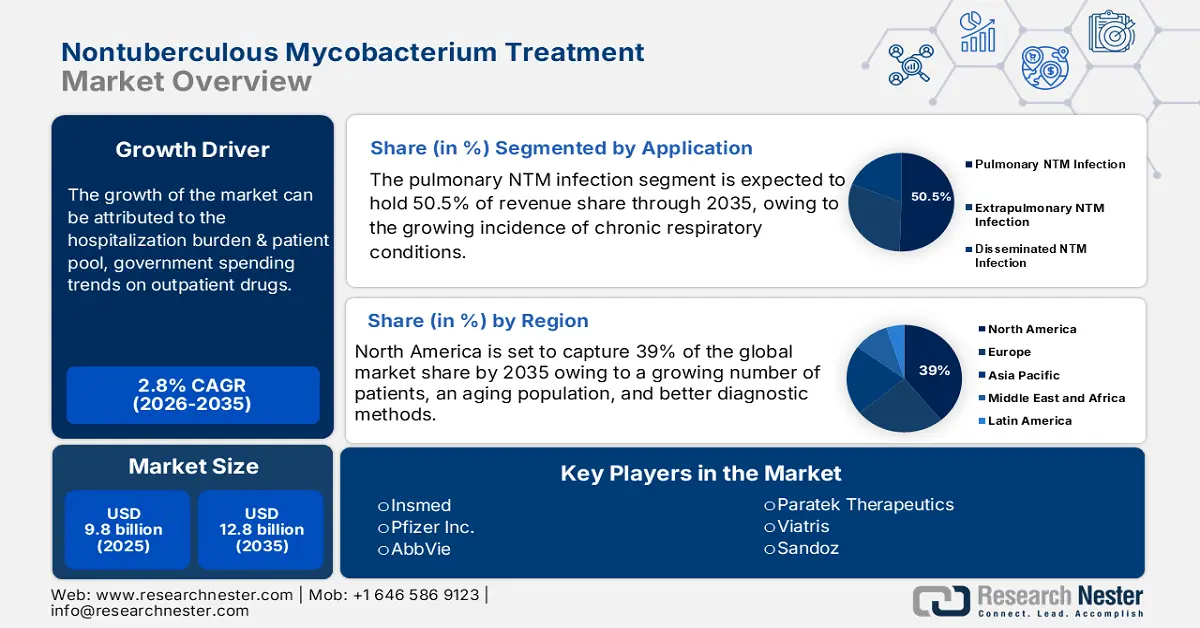
Nontuberculous Mycobacterium Treatment Market size was valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 12.8 billion by the end of 2035, rising at a CAGR of 2.8 % during the forecast period, i.e., 2026‑2035. In 2026, the industry size of nontuberculous mycobacterium treatment is evaluated at USD 10 billion.
The global nontuberculous mycobacterium treatment market is driven by an aging population and increased susceptibility in immunocompromised individuals. According to the American Lung Association report in October 2024, more than 86,000 people in the U.S. live with NTM lung disease, and this number is expected to rise more among women and the elderly population. This epidemiology directly informs the demand for complex, multi-drug regimens. The supply chain for NTM therapeutics is intricate, relying on a limited number of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) producers for core antibiotics like macrolides (e.g., azithromycin) and aminoglycosides (e.g., amikacin).
On the trade side, the U.S. imports raw materials critical to antimicrobial manufacturing, such as specialty chemicals and intermediates, principally from Europe and Asia, and exports finished pharmaceuticals to markets with established regulatory schemes. Therapy for nontuberculous mycobacterium (NTM) pulmonary disease generally consists of extended antimicrobial treatment, and first-line treatments include a three-drug regimen of a macrolide (e.g., azithromycin or clarithromycin), rifampin or rifabutin, and ethambutol. According to the BC Center of Disease Control Report, the success rate with the drugs is the highest of 65.7%, which reflects the complexity of treatment and the requirement for new approaches. The increasing burden on the patient population and treatment makes the market demand.