Fast Fashion Market Outlook:
Fast Fashion Market size was valued at USD 163.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 436.5 billion by the end of 2035, rising at a CAGR of 10.3% during the forecast period, i.e., 2026-2035. In 2026, the industry size of fast fashion is estimated at USD 180.6 billion.

The global fast fashion market is defined by the rapid-turnover and high-volume business model. They are completely relying on complex global supply chains and responsive production. The Invest India report in October 2025 has stated that the textile sector in India has exported more than USD 34.4 billion of textiles and apparel during the period of 2023 and 2024. This is fueled by the surging production cycle and rising consumer demand. This expanding industry encourages circular fashion and sustainable production to reshape the market ecosystem.
Market dynamics are propelled by the international trade patterns and evolving labor standards. According to the USITC report in September 2024, Cambodia, India, Bangladesh, Indonesia, and Pakistan together account for 27% of U.S. apparel imports. This reflects the substantial flow of goods. On the other hand, the regulatory bodies are focusing on supply chain transparency. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act in the U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act in the U.S. applies import restrictions on goods to a specific region, requiring companies to implement rigorous due diligence protocols to prove their supply chains are free from forced labor.
Key Fast Fashion Market Insights Summary:
Regional Insights:
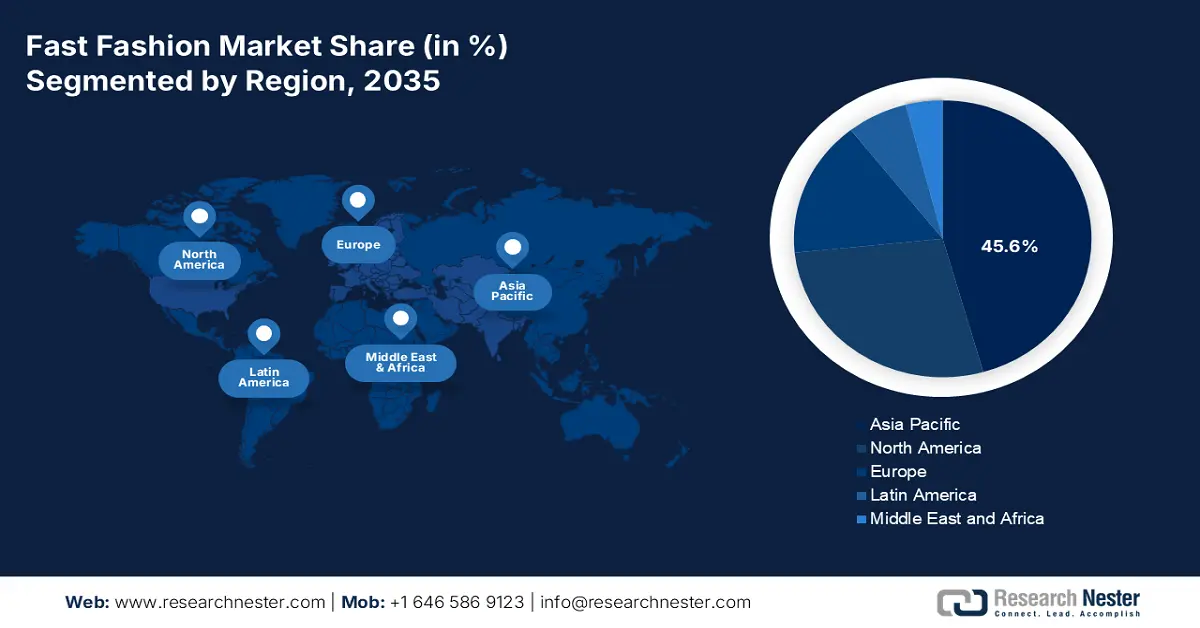
- By 2035, Asia-Pacific is projected to command a 45.6% share of the fast fashion market, supported by its massive manufacturing base and rapidly expanding consumer markets.
- North America is anticipated to sustain a substantial share by 2035, underpinned by high consumer spending and rapid adoption of digital channels.
Segment Insights:
- The conventional segment in the fast fashion market is poised to secure an 85.7% share by 2035, upheld by low price and immediate trend availability for the majority of the shoppers.
- The apparel segment is projected to dominate by 2035, fueled by its high purchase frequency and constant trend turnover.
Key Growth Trends:
- Increasing Disposable Income and Expanding Middle Class
- Economic tension and value-conscious consumption
Major Challenges:
- Supply chain transparency mandates
- Chemical safety and consumer health
Key Players: Inditex (Spain), H&M Group (Sweden), Bestseller (Denmark), Primark (UK), Mango (Spain), C&A (Germany), New Look (UK), River Island (UK), Gap Inc. (U.S.), Forever 21 (U.S.), American Eagle Outfitters (U.S.), Fast Retailing (Japan), Shein (China), Muji (Ryohin Keikaku Co., Ltd.) (Japan), Matsuya (Japan), E-land World (South Korea), Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail Ltd (India), Viva Goods Company (Hong Kong), Cotton On Group (Australia), Padini Holdings Berhad (Australia)
Global Fast Fashion Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 163.8 billion
- 2026 Market Size: USD 180.6 billion
- Projected Market Size: USD 436.5 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 10.3% CAGR (2026-2035)
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: Asia-Pacific (45.6% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: North America
- Dominating Countries: China, United States, India, United Kingdom, Germany
- Emerging Countries: Vietnam, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico, Turkey
Last updated on : 31 October, 2025
Fast Fashion Market - Growth Drivers and Challenges
Growth Drivers
- Increasing Disposable Income and Expanding Middle Class: Increasing disposable income, especially in emerging economies like India and China, boosts consumer spending on trendy fast fashion apparel. A rising middle class with more disposable income is a direct contributor to the demand for cheap and fashionable clothing options, thus making fast fashion more inexpensive and accessible globally. For example, as per the IBEF data in April 2025, the apparel market was valued at USD 106.9 billion in 2023. This reflects a strong growth connected to disposable income and urbanization. By fostering economic growth, governments indirectly support these same consumers in boosting their income and spending.
- Economic tension and value-conscious consumption: Rising economic pressures are surging the demand for cheap clothes, but with a difference in shipping costs. Consumers are seeking higher value, and they are increasingly favoring retailers that provide the lowest prices, without reducing the perceived quality. This favours giants like Primark based on its brick-and-mortar value proposition, and Uniqlo based on its focus on durable basics. Data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics shows clothing inflation usually lags overall inflation as many retailers cut prices to retain customers.
- Strategic shifts reshaping the fashion industry: The industry is actively adopting circular models and smart clothing tech to curb its environmental impact and minimize waste. To maintain a consistent flow of both materials and final products, companies are broadening their global sourcing networks and investing in more adaptable manufacturing systems. A parallel focus on ethical manufacturing and the use of wearable tech is also gaining traction, offering greater insight into supply chains and boosting corporate accountability. For example, a retailer's deployment of an AI-driven inventory system reportedly cut stock shortages and boosted revenue. Analysts project that such innovations will be a core driver, pushing the sector's growth into double digits in the near future.
Quantity of U.S. Apparel Imports
|
Supplier |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
|
Bangladesh |
1,809 |
2,449 |
2,860 |
2,093 |
|
India |
927 |
1,299 |
1,498 |
1,224 |
|
Indonesia |
928 |
1,115 |
1,338 |
981 |
Source: USITC August 2024
Challenges
- Supply chain transparency mandates: New laws like the U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) and EU due diligence laws require brands to map and monitor their entire supply chain for ethical violations. This represents a major constraint, as multi-tiered supply chains are common. Failure to comply results in seized shipments and reputational damage. Patagonia, while not being a typical fast fashion brand, collaborates with Footprint Chronicles, that is costly and difficult for new players to implement immediately.
- Chemical safety and consumer health: Various agencies have illustrated the connection between certain chemicals and health issues. This leads to the strict regulations like REACH in the EU. These regulations reduce the presence of harmful substances in textiles. Failure to meet the standards results in withdrawal of products from the market and prohibition of their distribution. For instance, C&A has introduced a strict manufacturing restricted substance list (MRSL) to ensure compliance; however, this entails a considerable expenditure on quality control and obtaining materials from certified sources, thereby creating a hurdle for those suppliers who have limited financial resources.
Fast Fashion Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Year |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
10.3% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 163.8 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 436.5 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Fast Fashion Market Segmentation:
Sustainability Claim Segment Analysis
Under the sustainability claim, conventional leads the segment and is poised to hold the share value of 85.7% by 2035. The segment is driven by the low price and immediate trend availability for the majority of the shoppers. This model faces rising pressure due to the environmental regulatory footprint. As per the UNEP March 2025 report, 92 million tons of textile waste are generated every year. The growing consumer shift toward eco-conscious fashion is expected to gradually redirect market momentum toward sustainable and recycled material alternatives over the forecast period.
Product Type Segment Analysis
Apparel dominates the product type segment and is propelled by the high purchase frequency and constant trend turnover. This segment's sheer size contributes significantly to textile waste streams. As per the EPA report in November 2024, the recycling rate for all textiles was 14.7%, with 2 million tons of waste recycled. This figure is anticipated to increase, underscoring the magnitude of the waste problem, as the fast fashion clothing market accounts for a significant amount of the total demand.
Price Point Segment Analysis
The budget sub-segment is the clear leader within the price point category, as accessibility remains the fundamental pillar of fast fashion's appeal to a global mass market. This relentless focus on low pricing, however, expresses the true environmental costs of production and disposal. The high consumption model typical for budget-priced products results in a cycle of frequent purchasing and discarding of garments. This creates a fundamental tension between the consumer demand for affordability and the pressing need for greater environmental sustainability within the industry.
Our in-depth analysis of the fast fashion market includes the following segments:
|
Segment |
Subsegments |
|
Product Type |
|
|
Consumer Group |
|
|
Price Point |
|
|
Distribution Channel |
|
|
Sustainability Claim |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Fast Fashion Market - Regional Analysis
APAC Market Insights
Asia-Pacific is the dominating region in the fast fashion market and is expected to hold the share of 45.6% by 2035. The region is driven by a massive manufacturing base and rapidly expanding consumer markets. Hyper-urbanization, a growing middle class with more disposable income, and the highest rates of mobile internet and e-commerce in the world are some of the main factors. A major trend is the rapid digital adoption, with social commerce and live-stream shopping becoming primary sales channels. Sustainability concerns are rising, but remain secondary to price and newness for many consumers. Further, governments have started to impose robust environmental regulations, hence forcing manufacturers to adopt greener practices.
China’s fast fashion market is expanding rapidly and is linked to its manufacturing dominance. As per the People’s Republic of China data in July 2025, the textile companies generated 1.49 trillion yuan, impacting a stable production base that supplies both global and domestic demand. This robust industrial output drives a highly competitive domestic market and is defined by the rapid rise of digital native brands and live stream shopping, hence creating an environment of speed and reach to consumers, a primary demanding metric.
India's fast fashion business is growing quickly due to the country's youthful population and government programs to support the country's textile industry. The Ministry of Textiles data in November 2024 depicts that the total share of man-made fibers exported in 2024 was 7%, highlighting the industry’s expanding capacity. Rising disposable incomes and legislative assistance are driving the growth of both domestic and foreign retailers, such as Reliance Trends, which are quickly expanding their store counts and online presence in order to meet the growing demand.
Estimated Production of Man-Made Fiber, Spun Yarn, and Filament Yarn
|
Period |
Man-made Fibre (Kg) |
Man-made Filament Yarn (Kg) |
Cotton Yarn (Kg) |
Blended & 100% Non-Cotton Yarn (Kg) |
Total Spun Yarn (Kg) |
|
2019-20 |
1,898 |
1,688 |
3,962 |
1,702 |
5,664 |
|
2020-21 |
1,610 |
1,326 |
3,625 |
1,521 |
5,146 |
|
2021-22 |
2,160 |
2,016 |
4,075 |
1,758 |
5,833 |
|
2022-23 |
2,152 |
1,904 |
3,438 |
1,746 |
5,184 |
|
2023-24 (P) |
1,987 |
1,702 |
3,756 |
1,725 |
5,481 |
|
2024-25 (April-Sept.) (P) |
1,021 |
904 |
1,868 |
884 |
2,752 |
Source: Ministry of Textiles November 2024
North America Market Insights
North America is leading the fast fashion market and is driven by the high consumer spending and rapid adoption of digital channels. Some of the main contributors are the e-commerce and social media marketing that facilitate consumer buying decisions and trend cycles. Sustainability is a very important aspect, as both consumers and regulators require more transparency. The market is very consolidated, and the major players are investing in omnichannel strategies, rental/resale models, and agile supply chains to be able to meet the customer's demand for speed and variety, while at the same time they are surrounded by increasing cost and regulatory pressures.
The U.S. fast fashion market is defined by hyper-competition and shortened product lifecycles, driven by digital-native brands and social media. The most noticeable trend is the regulatory push for the supply chain to be conducted with due diligence and sustainability. Data from the U.S. International Trade Commission in September 2024 showed that the U.S. is the largest importer of apparel, thus indicating that the sector is still growing in terms of the volume of trade. Besides, the country imported goods worth USD 79.3 billion, which were mainly produced in Asia. This underscores the U.S. market’s heavy reliance on overseas manufacturing.
Value of U.S. Imports of Apparel From China
|
Year |
Value (USD million) |
|
2020 |
18,728 |
|
2021 |
20,526 |
|
2022 |
21,922 |
|
2023 |
16,922 |
Source: USITC August 2024
The fast fashion market in Canada is driven by government-initiated circular economy policies and increased environmental awareness among consumers. A key trend is the development of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) frameworks for textiles. According to the Government of Canada data in July 2024, 290 kilotons of synthetic textile products were purchased in Canada. This points to the large quantity of synthetic fabrics in circulation and underscores the urgent need for sustainable production and recycling in the fast fashion industry.
Europe Market Insights
The fast fashion market in Europe is also expanding and is defined by a high degree of mature and intense competition. The key drivers of the market are the strong presence of dominating players such as Inditex (Zara) and H&M; these companies continuously innovate their supply chains for efficiency and speed. Regulations that promote sustainability and circularity are a prominent trend. As a result, more people are renting clothes, getting repairs done, and using recycled materials. Further, digital integration is vital to lead in omnichannel retailing and social commerce, driving sales.
The UK is estimated to lead the Europe market by its strong e-commerce capabilities and the urban consumers concentrated in a few areas. The main drivers are the rapid developments of ultra-fast fashion e-tailers such as Shein and Boohoo, which can attract customers through digital marketing and use data analytics for efficiency. In addition, the non-profit WRAP released data in January 2024, which states that just by extending the average clothing life by nine months, the carbon, water, and waste footprints can be reduced by 20%, saving £5 billion of resources every year. This figure is not only leading policy but also changing consumer behavior.
Germany's fast fashion market is one of the largest markets in Europe and is mainly driven by a demand for value that balances affordable quality and sustainability. German consumers are becoming eco-friendlier which is leading to a big trend towards circularity through the expansion of clothing rental, repair services, and a lively secondhand market. This shift is actively supported by government policy, such as the state-endorsed Green Button certification for sustainable textiles.
Key Fast Fashion Market Players:
- Inditex (Spain)
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- H&M Group (Sweden)
- Bestseller (Denmark)
- Primark (UK)
- Mango (Spain)
- C&A (Germany)
- New Look (UK)
- River Island (UK)
- Gap Inc. (U.S.)
- Forever 21 (U.S.)
- American Eagle Outfitters (U.S.)
- Fast Retailing (Japan)
- Shein (China)
- Muji (Ryohin Keikaku Co., Ltd.) (Japan)
- Matsuya (Japan)
- E-land World (South Korea)
- Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail Ltd (India)
- Viva Goods Company (Hong Kong)
- Cotton On Group (Australia)
- Padini Holdings Berhad (Australia)
- Inditex is the dominating player in the fast fashion market via various strategies such as a vertically integrated supply chain and a responsive business model. Its flagship brand, Zara, represents this strategy with a lightning-fast design-to-store process that can introduce new items in just weeks. As per the Inditex annual report, the net sales in 2024 reached €38,632 million.
- H&M Group leads by engaging in a multi-brand strategy. This is to capture diverse consumers from the core H&M brand to premium labels. Its focus is on scaling sustainability via investments in circularity, including garment collection and recycled material usage to meet the growing environmental needs. The company has increased the total number of outlets, which reached 4,253 in 2024.
- Bestseller is a major player in the fast fashion market and competes via empowered brand autonomy and a robust wholesale and franchise network. Its strategic initiatives are the considerable investment in digital transformation, aiming at data analytics to optimize the inventory and personalize customer engagement.
- Primark is one of the players in the fast fashion market and focuses on high volume, low margin, and a brick-and-mortar model. Its competitive edge stems from driving down costs, unparalleled economies of scale to provide the lowest possible prices without online sales.
- Mango has strategically positioned itself as the premium fast fashion segment. The company mainly focuses on higher-quality material and more advanced design than its key rivals. A critical initiative has been a massive investment in its online platform and logistics to bolster direct-to-consumer sales, especially during the pandemic.
Below is the list of some prominent players operating in the global market:
The fast fashion market is mainly influenced by the top contributors like Zara's parent, Spain's Inditex, and Sweden's H&M Group. Besides, the market is highly competitive because of digital giants such as Shein and Pinduoduo-owned Temu. These players have revolutionized the sector with ultra-low-cost and hyper-fast models. Further, the market is witnessing a strategic expansion into emerging economies. For example, the Bluestar Alliance announced its acquisition of Palm Angels in February 2025 on the purchase of luxury streetwear label Off-White from LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton.
Corporate Landscape of the Fast Fashion Market:
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, Prada Group announced that it had agreed to acquire 100% of Versace from Capri Holdings. The cash consideration is totally based on the Enterprise Value of €1.25 billion.
- In December 2024, Saks Fifth Avenue announced the acquisition of Neiman Marcus Group, which is the parent company of both Neiman Marcus and Bergdorf Goodman. The total enterprise value was USD 2.7 billion.
- Report ID: 8200
- Published Date: Oct 31, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Fast Fashion Market Report Scope
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




