Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture Market - Growth Drivers and Challenges
Growth Drivers
- High-tech precision farming solutions enhance crop management effectiveness: Premium AI-driven precision agriculture solutions enable farmers to optimize the use of resources such as water, pesticides, and fertilizers through real-time analysis and automated decision-making. Sophisticated systems can implement variable rate application technologies that adjust inputs according to field variation and crop requirements during planting seasons. In December 2024, AGCO Corporation demonstrated a groundbreaking suite of precision agriculture solutions through the PTx brand, empowering farmers to drive outcomes and improve productivity, as the sole company to successfully retrofit virtually any make or model of equipment with Precision Planting and PTx Trimble technology to produce more with less. The retrofit-first methodology maximizes total addressable market and accelerates technology adoption, providing more profitable farmers.
- Government investment initiatives drive technology uptake: Global government funding programs and policy frameworks support the mass adoption of AI in the agricultural sector through grants, subsidies, and technical assistance plans. Strategic public-private partnerships enable knowledge sharing and technology transfer, making it available to diverse farming operations, such as smallholder farmers. In August 2025, the United States National Science Foundation launched AI-ENGAGE (Advancing Innovations for Empowering NextGen AGriculturE) Initiative with the support of Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), and Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization of Australia (CSIRO). The initiative anticipates farmers using apps backed by affordable sensors, robots, and artificial intelligence to access precise real-time information regarding water, fertilizer, and pest needs.
- Data-driven decision-making transforms farm operations: Artificial intelligence-powered analytics software consumes massive amounts of farm data from diverse inputs like weather stations, soil sensors, and crop monitoring systems to provide actionable recommendations for ideal farm decisions. In October 2023, DigiFarm's cloud-native precision agriculture software was supported by Oracle Corporation on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, which enabled farmers and agribusinesses to automatically identify field boundaries from high-resolution satellite imagery and employ neural network models to compute seeded field acreage boundaries. Predictive algorithms continuously improve prediction accuracy while providing real-time suggestions for changes in operations and optimizing resources.
Accuracy of AI Models in Plant Disease and Pest Detection
|
AI Model / System Name |
Crop / Scope |
Reported Accuracy (%) |
Key Technology |
|
CNN Model |
25 different plants |
99.53% |
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) |
|
ResNet-50 |
General plant disease & pest |
95.61% |
ResNet-50 (Deep Residual Network) |
|
PlantDoc |
13 plant species |
- |
Computer Vision / Deep Learning |
|
Agpest Expert System |
Wheat & Rice |
- |
ANN, Genetic Algorithm, Computer Vision |
|
Alternative Diagnostic Methods |
General |
~75% |
Traditional lab/visual analysis |
Source: PMC
Development and Deployment of AI Technologies in Agriculture
The adoption of robotic and digital technologies in agriculture is rapidly advancing, moving from research and limited trials toward broader commercialization. While technologies like GPS-guided machinery are now widespread, autonomous field robots for tasks such as weeding and crop scouting are currently used by only 2–4% of agricultural input dealerships. However, significant growth is anticipated, with nearly one-fifth of dealers offered robotic crop scouting services in 2024, signaling a major shift toward automated and precision farming solutions.
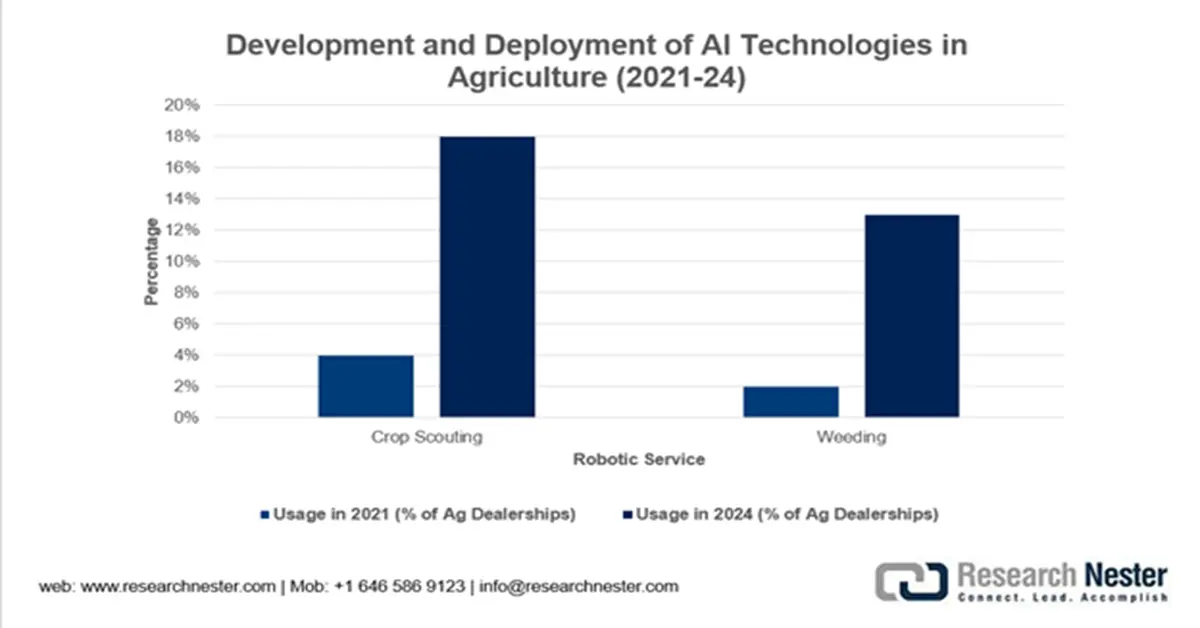
Source: DOI
Challenges
- Technical complexity of technology integration hinders mass adoption: Sophisticated AI models require sophisticated technical infrastructure and specialized expertise for effective implementation and maintenance across various types of agricultural operations. The majority of farming operations lack the necessary technical capabilities and infrastructure to effectively incorporate advanced AI systems within the current equipment and management systems. Rural communities of farmers often suffer from poor connectivity and inadequate technical support services, which hinder the effective deployment and implementation of AI. This results in significant investment for training and education programs to provide farmers with the necessary knowledge to unlock the potential of AI. Furthermore, a more accessible and adaptable set of AI solutions needs to be developed for widespread adoption in agriculture.
- Technology adoption gets hindered by data security and privacy concerns: Farming AI solutions gather huge amounts of personalized farm data like field settings, crop yields, and agricultural practices that pose grave issues regarding farmers' privacy and data security. Security issues breaching agricultural data and control systems threaten agricultural practices and food security infrastructure even further. In July 2023, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) published guidelines on establishing a national test-farm Internet of Things (IoT) network to enhance agricultural production while promoting sustainable practices. Specific application areas include yield prediction, pest management, disease management, irrigation scheduling, and supply chain optimization.
Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture Market Size and Forecast:
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Year |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
26% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 3 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 30.2 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|

