Posted Date : 15 October 2025
Posted by : Sanya Mehra
In a fast-paced world of logistics and supply chain management, efficiency is the cornerstone of success. Warehouses, the important hubs for storage and distribution, are undergoing a technological revolution, with Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) leading the charge. These self-operating machines are reshaping how goods are moved, stored, and managed, driving productivity, safety, and cost savings. This blog highlights how AGVs are transforming warehouse operations, supported by real-world applications, to provide a comprehensive understanding of their impact.
What Are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)?
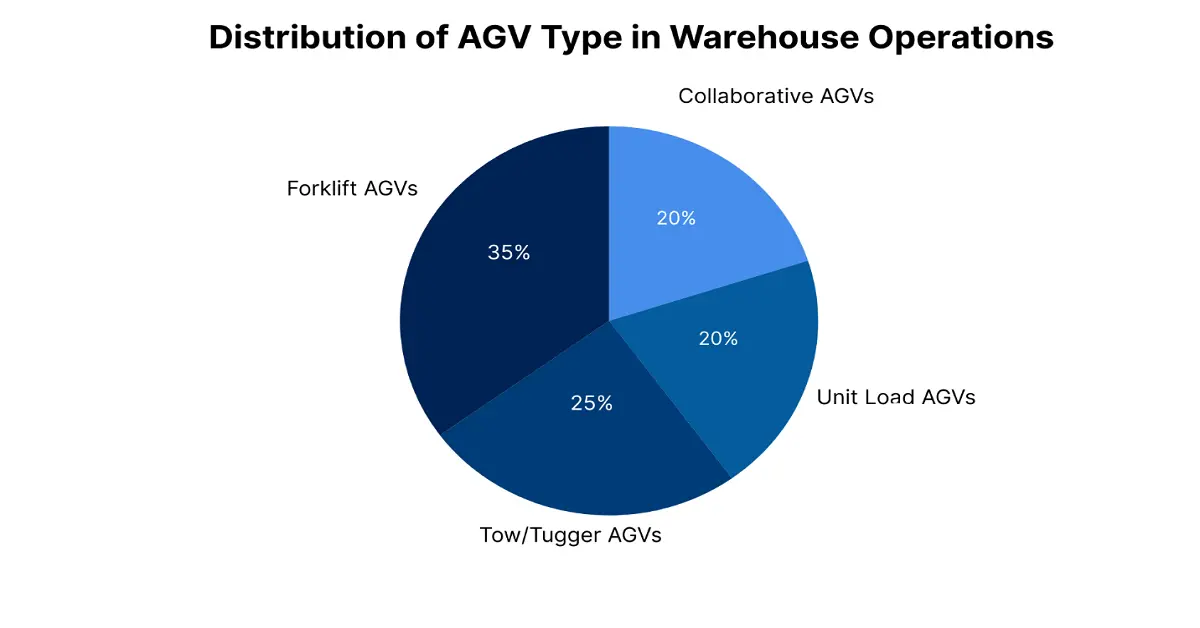
Automated Guided Vehicles are mobile robots made to transport materials within a facility without human intervention. They navigate using predefined paths or advanced technologies, namely laser guidance, magnetic strips, or vision-based systems. AGVs are fitted with sensors, cameras, and software that help them move safely and efficiently, avoiding obstacles and following optimized routes. AGVs exist in multiple variants, such as:
- Forklift AGVs: For lifting and transporting pallets.
- Tow/Tugger AGVs: For pulling carts or trailers.
- Unit Load AGVs: For carrying individual items or small loads.
- Collaborative AGVs: Designed to work alongside human operators.
According to a 2023 report by Research Nester, the global AGV market was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2024 and is predicted to reach USD 3.5 billion by 2035, increasing at a CAGR of 6.4% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by the rising demand for automation in warehouses, especially in e-commerce and manufacturing.
The Need for AGVs in Modern Warehouses
The warehouse industry faces rising pressure to fulfill consumer demands for faster delivery, higher accuracy, and lower costs. The e-commerce sector, in particular, has faced huge growth, with global online retail sales anticipated to hit $7.4 trillion by 2025, according to Research Nester. This surge has strained traditional warehouse operations, which rely heavily on manual labor and are prone to inefficiencies, errors, and safety risks. The existing challenges in traditional warehouses led to the introduction of AGVs that are transforming movement in warehouses. A few of the challenges are as follows:
- Labor Shortages: The logistics sector faces a global shortage of skilled workers, with the U.S. alone predicted to experience a lack of 2 million warehouse workers by 2030, per a study by the National Association of Manufacturers.
- Rising Operational Costs: According to the Warehousing Education and Research Council (WERC), manual processes increase labor costs, which account for 50-70% of warehouse operating expenses.
- Safety Concerns: Forklift accidents and repetitive strain injuries result in thousands of workplace incidents annually, with OSHA reporting over 85,000 forklift-related accidents in the U.S. every year.
AGVs address these challenges by automating repetitive tasks, reducing labor dependency, and improving safety through precise navigation and collision avoidance.
How AGVs Revolutionize Warehousing
- Enhanced Efficiency and Outcome: AGVs improve material handling by automating functions such as picking, transporting, and sorting. Unlike human workers, AGVs work continuously 24/7 without downtime, notably increasing output. In 2023, Amazon deployed over 750,000 robots, including AGVs, across its fulfillment centers, resulting in a 25% increase in order processing speed compared to traditional manual operations.
AGVs also optimize workflows through integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). For instance, AGVs can concentrate on tasks based on real-time inventory data, reducing idle time and assuring just-in-time delivery of goods. A 2022 study by Logistics Management found that warehouses using AGVs reported a 30% reduction in order fulfillment times. - Better Accuracy and Reduced Errors: Human picking and transportation are very likely to make errors, such as misplacing items or delivering incorrect products. AGVs, guided by precise navigation systems, achieve near-perfect accuracy. For instance, DHL Supply Chain highlighted a 99.9% order accuracy rate after using AGVs in its warehouses in North America. This precision lowers costly returns and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings Over Time: While the initial investment in AGVs can be noteworthy, i.e., ranging from $20,000 to $100,000 per unit, depending on complexity, the long-term savings are substantial. AGVs decrease labor costs by automating repetitive tasks, helping companies to reallocate human workers to higher-value roles like inventory analysis or customer service. Additionally, these AGVs decrease energy expenses compared to traditional forklifts. Electric-powered AGVs consume less energy and require minimal maintenance, contributing to a lower total cost of ownership.
- Enhanced Safety: AGVs are created with advanced safety features, including LiDAR sensors, cameras, and emergency stop systems, to prevent collisions and accidents. By lowering the need for human-operated forklifts, AGVs decrease workplace injuries. A 2021 study by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) found that warehouses using AGVs reported a 60% reduction in material handling-related injuries.
- Scalability and Flexibility: AGVs are highly adaptable to changing warehouse needs during peak times. For example, in the 2022 holiday season, Walmart deployed extra AGVs in its distribution centers, increasing productivity by 15% while avoiding the need for temporary seasonal hiring.
Practical Uses of AGVs
- Top E-Commerce Giants: E-commerce companies, like Amazon and Alibaba, have implemented AGVs to handle massive orders. Amazon implements Kiva robots to transfer shelves directly to laborers, saving walking time and improving final results. Similarly, Alibaba’s Cainiao network also uses AGVs for package grouping and moving, handling near about 1 million orders daily during peak time.
- Automotive Sector: Automotive companies, like Toyota and BMW, depend on AGVs to ensure the on-time delivery of components to their assembly lines. Toyota’s AGVs, built with its Just-In-Time production system, have decreased inventory holding expenditures by 30%, according to a 2023 case study report.
- Pharmaceutical Warehouses: In temperature-controlled environments, AGVs ensure the accurate handling of sensitive goods. Pfizer’s distribution centers use AGVs to transport vaccines and medications, maintaining strict compliance with regulatory standards while minimizing manual error.
The Future of AGVs in Warehouses
The transformation of AGVs is far from over. Given below are some emerging technologies that are improving their capabilities:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered AGVs can learn from their environment, optimize routes in real-time, and predict maintenance needs.
- 5G Connectivity: 5G enables faster data transfer, helping AGVs to communicate smoothly with WMS and IoT devices, improving coordination in large warehouses.
- Swarm Robotics: Inspired by nature, swarm AGVs work collectively to handle complicated tasks, increasing efficiency in high-volume environments.
The rise of Industry 4.0 is also boosting AGV adoption. The International Federation of Robotics predicts that 50% of global warehouses will include some form of automation by 2030.
Conclusion
AGVs are revolutionizing warehouse operations, offering unmatched efficiency, precision, and safety. As e-commerce and global supply chains continue to expand, AGVs are likely to play an important role in fulfilling demand while reducing costs and environmental impact. By adopting this technology, businesses can stay competitive in an increasingly automated world. Whether you are a small warehouse or a global logistics giant, AGVs are a game-changer in this discipline worth exploring.
Contact Us







