Satellite Internet Market Outlook:
Satellite Internet Market size was valued at USD 12.4 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 47.4 billion by the end of 2035, rising at a CAGR of 14.3% during the forecast period, i.e., 2026-2035. In 2026, the industry size of satellite internet is estimated at USD 14.2 billion.

The market represents a critical infrastructure segment focused on providing broadband connectivity to global regions where terrestrial networks are economically or geographically unfeasible. Government and intergovernmental data indicate that satellite internet remains a structurally important connectivity layer for enterprise, government, and critical infrastructure use cases, mainly where the terrestrial networks are economically or physically constrained. The data from the Country Health Rankings & Roadmaps 2025 has indicated that nearly 14.5 million locations in the U.S. lack access to fixed terrestrial broadband at benchmark speeds, with the rural and Tribal areas accounting for a disproportionate share of the gap, reinforcing institutional reliance on satellite-based services for continuity and coverage assurance.
The National Telecommunications and Information Administration further notes that satellite services are routinely incorporated into the federal connectivity strategies for emergency response maritime operations, aviation, and defense-related communications, where redundancy and geographic reach are prioritized over latency sensitivity. The ITU in November 2024 reported that nearly 2.6 million people remain offline, primarily in low-density or remote regions, positioning satellite internet as a necessary component of national broadband and universal service frameworks rather than a substitute for fiber or mobile networks. Further, the focus extends to space sustainability, with the Federal Communications Commission adopting its first-ever orbital debris mitigation rules in 2022 for the U.S.-licensed satellites, introducing new compliance parameters for operators. This regulation defines a market shift from niche applications to a core component of national and global broadband infrastructure.
Key Satellite Internet Market Insights Summary:
Regional Highlights:
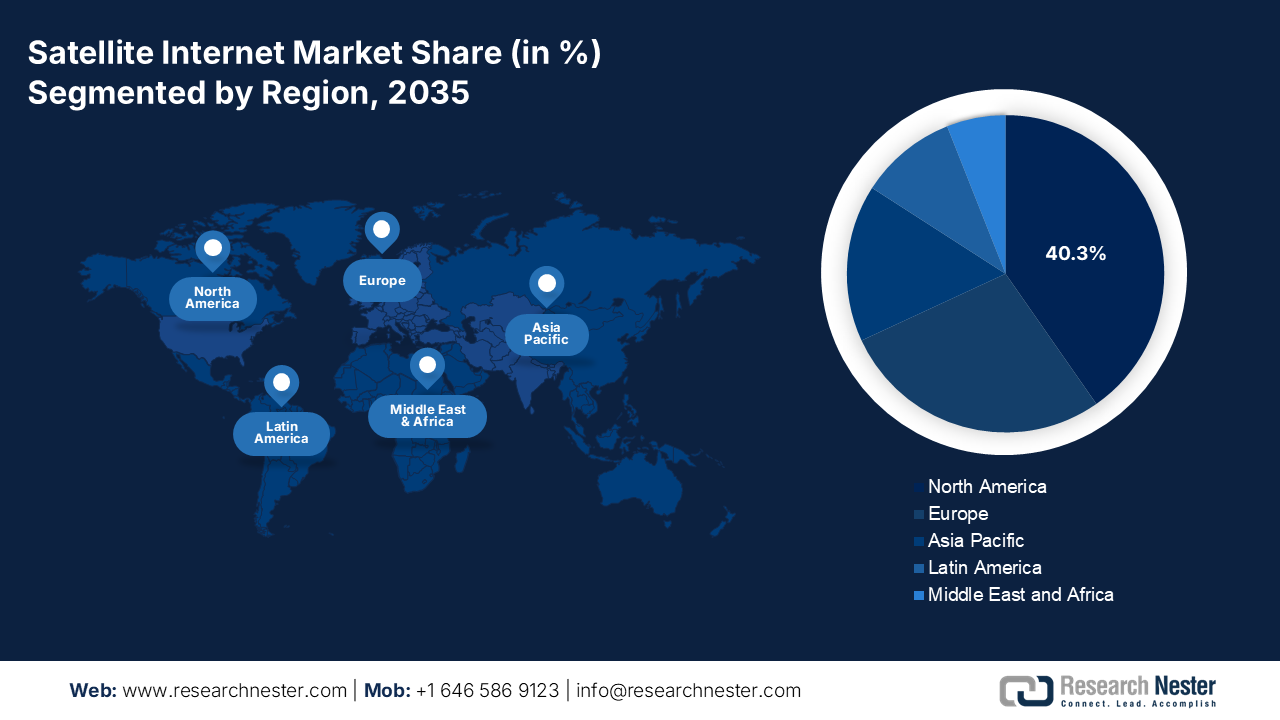
- North America in the satellite internet market is projected to secure a 40.3% revenue share by 2035, anchored by strong consumer uptake, leading constellation operators, and sustained public-sector funding momentum catalyzed by large-scale universal broadband initiatives.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to expand at a 16.3% CAGR during 2026–2035, strengthened by vast unserved populations, ambitious digitalization programs, and accelerating satellite–terrestrial network convergence.
Segment Insights:
- Under the application segment, communication and data transfer in the satellite internet market are projected to capture a 65.4% share by 2035, underpinned by their essential role in global connectivity across enterprise WANs, government networks, and IoT ecosystems, stimulated by the rise of direct-to-cellular satellite services.
- In the orbit segment, low Earth orbit is anticipated to command the largest share by 2035, supported by its ability to deliver low-latency connectivity suitable for real-time digital applications, reinforced by the large-scale deployment of LEO satellite constellations.
Key Growth Trends:
- National security, defense and government resilience requirements
- Government broadband subsidies and universal service funding
Major Challenges:
- Complex regulatory and spectrum licensing hurdles
- Launch capacity and logistics bottlenecks
Key Players: Signify, Osram Licht AG, Zumtobel Group, Acuity Brands, FSL Lighting, GE Lighting, Eaton Lighting, NVC Lighting, Zhejiang Yankon Group, Panasonic Lighting, Cree Lighting, Logos Lighting, Toshiba Lighting, Sharp Electronics, Seoul Semiconductor
Global Satellite Internet Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 12.4 billion
- 2026 Market Size: USD 14.2 billion
- Projected Market Size: USD 47.4 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 14.3% CAGR (2026-2035)
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: North America (40.3% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Asia Pacific
- Dominating Countries: United States, China, Japan, Germany, United Kingdom
- Emerging Countries: India, Brazil, Indonesia, Vietnam, Saudi Arabia
Last updated on : 24 December, 2025
Satellite Internet Market - Growth Drivers and Challenges
Growth Drivers
- National security, defense and government resilience requirements: Defense and homeland security agencies are integrating the satellite internet into the secure and resilient communications architecture. The U.S. CSPS June 2024 report depicted that the FY 2025 Space Force budget request of USD 29.6 billion directly relates to the market through allocations for proliferated satellite constellations, resilient SATCOM, and commercial integration. NATO and allied governments similarly emphasize satellite networks for command, control, logistics, and cross-border coordination, mainly under the degraded terrestrial network conditions. Satellite internet also supports border surveillance, disaster response, and continuity of government operations. The demand in this segment prioritizes assured capacity, geographic redundancy, and compliance with defense-grade procurement standards, favoring providers capable of long-term service assurance rather than low-cost access models.
Space Force Budget Growth (2021-2025)
|
Year |
Budget (USD billion) |
|
2021 |
15.3 |
|
2022 |
18.0 |
|
2023 |
26.3 |
|
2024 |
28.9 |
|
2025 |
29.6 |
Source: CSPS June 2024
- Government broadband subsidies and universal service funding: The public funding mechanisms are a primary demand accelerator for satellite internet adoption. In the U.S., the FCC in December 2024 indicated that the process for large satellites can cost up to USD 500 million. This budget directly affects the capacity expansion, pricing, and supplier concentration in the satellite internet services. These costs determine which firms can deploy and sustain satellite broadband infrastructure. Further, the government-backed broadband programs across North America and Europe are expected to support the connectivity for remote premises, with satellite forming a core delivery mode in the highest-cost geographies. Satellite operators that demonstrate compliance with subsidy performance, reporting, and service-level obligations are best positioned to secure multi-year government contracts.
- Resilience as a critical infrastructure requirement: Resilience is now a formal requirement for the critical infrastructure mandated by the government policy and corporate governance. Following major cyber-attacks and natural disaster sectors such as finance, energy, and emergency services must maintain operations during the terrestrial network failures. This shifts satellite communications from a contingency tool to a core integrated component of enterprise risk management and software-defined wide area network architectures. The result is a predictable recurring demand for resilience as a service, dedicated high availability satellite links that ensure continuity. This driver creates a stable B2B market less sensitive to consumer pricing, focused on guaranteed uptime and seamless failover capabilities for essential services.
Challenges
- Complex regulatory and spectrum licensing hurdles: Gaining national and international regulatory approval for the spectrum use and orbital slots is a multi-year, complex process. Entrants must navigate bodies such as the ITU and national regulators. Amazon’s Project Kuiper has spent years securing its FCC license, which was granted under strict conditions, including a requirement to launch its satellite constellation. Failure to meet the deadlines can result in the license revocation, creating a high-stakes timeline.
- Launch capacity and logistics bottlenecks: Access to affordable, reliable launch services is a major bottleneck. The global launch manifest is crowded, and new entrants compete with the established players, such as SpaceX, for slots. AST SpaceMobile, building a cellular broadband constellation, has faced significant delays due to launch scheduling and readiness, pushing back its operational timeline and impacting investors' expectations, and illustrating how launch logistics are a vital path dependency.
Satellite Internet Market: Key Insights
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Year |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
14.3% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 12.4 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 47.4 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Satellite Internet Market Segmentation:
Application Segment Analysis
Under the application segment, the communication and data transfer are leading the segment in the market and are poised to hold the share value of 65.4% by 2035. The segment is driven by the foundational need for global connectivity serving enterprise WANs, government networks, and the rapidly expanding Internet of Things. A key growth driver is the direct-to-cellular service, where the satellites connect to standard mobile devices. The U.S. government is the major catalyst, with agencies such as the National Telecommunications and Information Administration allocating billions to close connectivity gaps. For example, the report from Broadband USA in June 2023 stated that NITA’s Broadband Equity Access and Deployment Program, which funded over USD 42.45 billion, explicitly includes satellite solutions as a viable technology for providing service in unserved areas, ensuring its continued financial and strategic importance.
Orbit Segment Analysis
In the orbit segment, the low Earth orbit is dominating the segment and is forecasted to hold the largest share by 2035 in the satellite internet market. The segment is driven by its critical advantage of low latency, which enables real-time applications such as video calls, online gaming, and cloud computing that are impractical with traditional GEO satellites. The scale of deployment is staggering the Federal Communications Commission actively tracks its growth. As of 2023, the authorization update, the FCC report in December 2022, had approved and was processing applications for constellations totaling tens of thousands of new LEO satellites, with SpaceX’s Starlink alone authorized for launch of nearly 12,000 satellites and seeking approval for up to 30,000 more, illustrating the massive capital and operational shift toward this orbit.
Bandwidth Segment Analysis
Ka-band is the leading sub-segment by bandwidth, expected to hold the maximum share in the market. This high-frequency band is the cornerstone of modern high-throughput satellite systems due to its ability to provide greater capacity and higher data speed for both fixed and mobile services. Its adoption is central to new LEO constellations such as Starlink and Kuiper. The government licensing reflects its focus. For instance, the FCC’s detailed allocation tables show that a significant portion of new satellite systems authorization from 2022-2024 were for operations in the Ka band, as it offers the spectral efficiency needed to meet the soaring global demand for broadband. A key statistical indicator is that the majority of the new satellite internet user terminals are deployed in this period, numbering in the millions, and are designed to operate in the Ka-band.
Our in-depth analysis of the market includes the following segments:
|
Segment |
Subsegments |
|
Service Type |
|
|
Platform |
|
|
End user |
|
|
Band Width |
|
|
Orbit |
|
|
Application |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Satellite Internet Market - Regional Analysis
North America Market Insights
North America market is expected to hold the revenue share of 40.3% by 2035. The market is driven by the high consumer adoption, significant government spending, and the presence of the leading constellation operators such as SpaceX and ViaSat. The key trends include the rapid deployment of the low-earth orbit networks providing low-latency broadband and strategic integration with the 5G infrastructure. A primary demand driver is the U.S. government’s massive investment in the universal broadband exemplified by the BEAD program that recognizes satellite as a vital solution for the unserved rural and remote communities. Further, stringent federal procurement for the resilient and mobile defense communications provides a stable, high-value revenue stream. In Canada, parallel national initiatives focus on connecting the most remote northern and indigenous communities.
The U.S. is the dominant player in North America in the satellite internet market. The trend is the convergence of the public subsidy programs and the commercial deployment of LEO. The report from Congress.gov in November 2024 has depicted that the shift from the GEO-based broadband to commercially viable LEO satellite deployments enabled by declining launch costs and electronics miniaturization, and marked by the start of LEO broadband services, directly expands service performance, coverage economics, and addressable demand, thereby accelerating government and enterprise adoption and driving overall market growth. Since the start of LEO broadband services, multiple U.S. based providers have advanced large-scale constellation deployments aimed at national and global connectivity. Further, the integration of satellite connectivity into terrestrial 5G networks and consumer devices is moving the technology from a standalone backup to an embedded component of the national communications infrastructure.
Major GEO and LEO Satellite Providers in the U.S.
|
Provider |
Download Speeds |
Upload Speeds |
Latency |
Lifespan |
|
Amazon (LEO) |
400 Mbps-1 Gbps |
Unknown |
Unknown |
5 years |
|
SpaceX (LEO) |
25-220 Mbps |
5-20 Mbps |
25-100+ ms |
5 years |
|
Hughes Network Systems (GEO) |
Up to 100 Mbps |
5 Mbps |
Low |
15 years |
|
Viasat (GEO) |
Up to 150 Mbps |
3 Mbps |
638 ms |
15 years |
Source: Congress.gov in November 2024
In Canada, the satellite internet market is defined by the geography-driven public policy and strategic investment in the sovereign space capacity. The central trend is executing the universal broadband fund’s USD 3.225 billion mandate to connect all the people in Canada by 2030, with satellite as the essential solution for the remote North and Indigenous communities, based on the Government of Canada report in August 2025. This public investment is uniquely coupled with the direct federal support for the domestic Telesat Lightspeed LEO constellation to create a dedicated national capacity and service guarantees for high-cost service areas. This model of using public capital to de-risk the critical domestic infrastructure ensures connectivity in strategically vital regions such as the Arctic. The market is a clear example of satellite internet being deployed as a public utility for national cohesion and sovereignty.
APAC Market Insights
The Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing market and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.3% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035. The market is driven by the massive unserved population, expansive geography, and aggressive government digitalization agendas. Unlike mature Western markets, growth here is propelled by the combination of bridging the urban-rural digital divide and meeting the explosive data demands of maritime aviation and enterprise sectors. China and India are the two markets focusing on sovereign constellation networks for strategic autonomy, and India is leveraging public-private models to connect hundreds of thousands of villages. A key regional trend is the focus on integrated satellite-terrestrial networks with mobile operators partnering with the satellite providers to extend coverage. Japan and South Korea, while having high terrestrial penetration, are driving innovation in satellite-enabled IoT and 5G backhaul, positioning the region as both a volume market and a technology incubator.
China’s satellite internet market is strategically driven by the state-led initiatives to achieve technological sovereignty and secure communications. The central project is the GuoWang constellation led by the state-owned China Satellite Network group, aiming to deploy over 12,992 LEO satellites. This initiative is a core component of the national digital infrastructure designed to provide autonomous coverage for the civilian and strategic needs, including the remote regions and the Belt and Road initiative. For illustrative purposes, the data from the IFRI in April 2023 indicates that the investment, which explicitly includes the satellite internet and the space-ground integrated networks, was a key allocation in the national plans, with the related sector investment exceeding USD 20 billion. This massive investment ensures China will dominate the regional market, focusing on the closed loop ecosystem development domestics manufacturing, and export of integrated solutions.
India’s market is characterized by explosive growth through public-private partnerships aimed at bridging a vast digital divide. The government’s Digital India and rural broadband initiatives create a foundational demand, with the satellite positioned as the key technology for connecting villages. A move was the partnership between the government’s commercial arm, NewSpace India Limited, and OneWeb to deliver pan-India LEO broadband services. This model uses the ISRO’s launch capabilities and private sector agility. A report from the PIB in July 2025 depicts that for the year 2023 to 2024, the Department of Space was allocated ₹12,543.91 crore, with a significant portion directed toward satellite communication and navigation projects. This public funding, combined with the private investment, positions India as the world's second-largest and fastest-growing national market.
Department of Space Budget Allocation
|
Year |
Budget |
|
2021-2022 |
13949.09 |
|
2022-2023 |
13700.00 |
|
2023-2024 |
12543.91 |
|
2024-2025 |
13042.75 |
|
2025-2026 |
13416.20 |
Source: PIB July 2025
Europe Market Insights
Europe in the satellite internet market is a mature yet strategically evolving segment driven by the European Union’s policy objective of achieving a gigabit society by 2030. This goal mandates universal high capacity connectivity positioning satellite technology as the vital solution for covering the continent's persistent rural and remote coverage gaps that terrestrial networks cannot address cost-effectively. A key trend is the strong integration of satellite into secure government satellite communications programs for defense and institutional use, with significant national investments from countries such as Germany and France. The market is also characterized by the rise of pan-European commercial initiatives, such as the partnership between Eutelsat (France) and OneWeb (UK), creating a multi-orbit service provider to offer integrated GEO and LEO services.
Germany is leading the market and is driven by the government and enterprise demand for secure, resilient communications rather than mass consumer broadband. The report from the DECIX data in November 2025 has demonstrated that 58% of the population in Germany is already aware of the satellite-based internet services, yet actual usage remains limited at around 5%, indicating that the market is still in an early adoption phase. The demand elasticity is strong; approximately 70% of the respondents expressed willingness to use satellite internet if consistent connectivity quality could be guaranteed, regardless of the location, highlighting the substantial latent demand. This gap between the awareness trial and intent underscores a clear growth opportunity tied to service reliability, performance assurance, and integration into national broadband strategies.
The UK satellite internet market is defined by the strategic pivot to sovereign space capabilities following its departure from the EU, with the government’s acquisition of OneWeb serving as the central pillar. This move is a part of the broader National Space Strategy aimed at securing independent global connectivity, boosting the domestic space industry, and providing resilient services for defense and government. The UK’s focus extends to becoming a leader in space sustainability and regulation. Beyond the stat-backed constellation, there is a significant commercial activity in satellite manufacturing, ground segment technology, and launch services. Further, the UK government invested in space based connectivity initiatives, underscoring the scale of the public commitment. This positions the UK to capture a leading share in the European market through a unique model of direct state ownership in a global commercial operator, balancing sovereign control with commercial ambition.
Key Satellite Internet Market Players:
- Starlink (SpaceX) (U.S.)
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- Viasat (U.S.)
- Hughes Network Systems (EchoStar) (U.S.)
- Amazon (Project Kuiper) (U.S.)
- OneWeb (UK)
- SES (Luxembourg)
- Eutelsat Group (France)
- Telesat (Canada)
- Inmarsat (Viasat-owned) (UK)
- Thales Alenia Space (France/Italy)
- Airbus Defence and Space (Europe)
- AST SpaceMobile (U.S.)
- Boeing Satellite Systems (U.S.)
- Lockheed Martin Space (U.S.)
- Northrop Grumman (U.S.)
- Mitsubishi Electric (Japan)
- SKY Perfect JSAT (Japan)
- Hanwha Systems (South Korea)
- ISRO / NSIL (India)
- MEASAT (Malaysia)
- Starlink is revolutionizing the global satellite internet market with its rapidly deployed low-earth-orbit mega constellation. This initiative is breaking the geographical barriers by delivering high-speed, low-latency broadband directly to consumers, enterprises, and remote communities worldwide, thereby creating unprecedented competition for terrestrial and traditional satellite providers.
- ViaSat is a dominant player in the satellite internet market, leveraging its high-capacity government sector. Following its acquisition of Inmarsat, ViaSat is strategically integrating the GEO and LEO assets to offer a robust global hybrid network that ensures resilient connectivity for critical applications. The company has witnessed a revenue of USD 4.3 billion in 2024.
- Hughes Network Systems is a foundational player in the North American satellite internet market, operating the largest satellite-based consumer broadband service. Hughes is advancing its strategic position by developing the Jupiter 3, one of the world’s most powerful commercial GEO satellites, to expand capacity and meet the growing residential and enterprise demand for high-throughput internet.
- Amazon is poised to be a transformative competitor in the satellite internet market with its planned multi-billion-dollar LEO constellation. The company's strategic initiative focuses on integrating space-based connectivity with the Amazon Web Services cloud infrastructure, aiming to provide a scalable, low-latency broadband to the unserved and underserved global communities and enterprise customers.
- OneWeb is a key architect in the evolving satellite internet market, having completed its first-generation LEO constellation to deliver global connectivity. Its strategic partnership with Eutelsat and collaborations with telecom operators worldwide are designed to provide backhaul and enterprise-grade internet services, positioning it as a crucial wholesale and government connectivity provider. The company has generated a net cash of INR 162, 936 K in 2024.
Here is a list of key players operating in the global market:
The satellite internet market is defined by a fierce race between the low-earth-orbit and the established geostationary operators. Companies such as Starlink lead the LEO revolution with the aggressive deployment and vertical integration, while OneWeb and Amazon Kuiper pursue large-scale constellations. The traditional giants, such as Viasat and Eutelsat, are merging assets and integrating GEO with the MEO/LEO networks to offer seamless global services. The key strategic initiatives include vertical integration, strategic partnerships, hybrid network development, and securing crucial spectrum rights. For example, in March 2025, Jio Platforms Limited (JPL) announced an agreement with SpaceX to offer Starlink’s broadband internet services to customers in India. In Asia, players such as SKY Perfect JSAT and NSIL focus on regional dominance and government partnerships, creating a multi-layered global contest for connectivity.
Corporate Landscape of the Satellite Internet Market:
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, SES announced that it had completed the acquisition of Intelsat, creating a global multi-orbit connectivity powerhouse with an expanded fleet of 120 satellites across two orbits.
- In July 2025, Union Communications Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia announced that Elon Musk-led Starlink has received a license to launch a satellite internet service in India, and a framework for spectrum allocation is also in place for a smooth rollout.
- In March 2025, Airtel announced an agreement with SpaceX to bring Starlink’s high-speed internet services to its customers in India. This is the first agreement to be signed in India, which is subject to SpaceX receiving its own authorizations to sell Starlink in India.
- Report ID: 3707
- Published Date: Dec 24, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Satellite Internet Market Report Scope
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




