Ruthenium Recycling Market Outlook:
Ruthenium Recycling Market size was valued at USD 552.02 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 1.47 billion by 2035, registering around 10.3% CAGR during the forecast period i.e., between 2026-2035. In the year 2026, the industry size of ruthenium recycling is evaluated at USD 603.19 million.
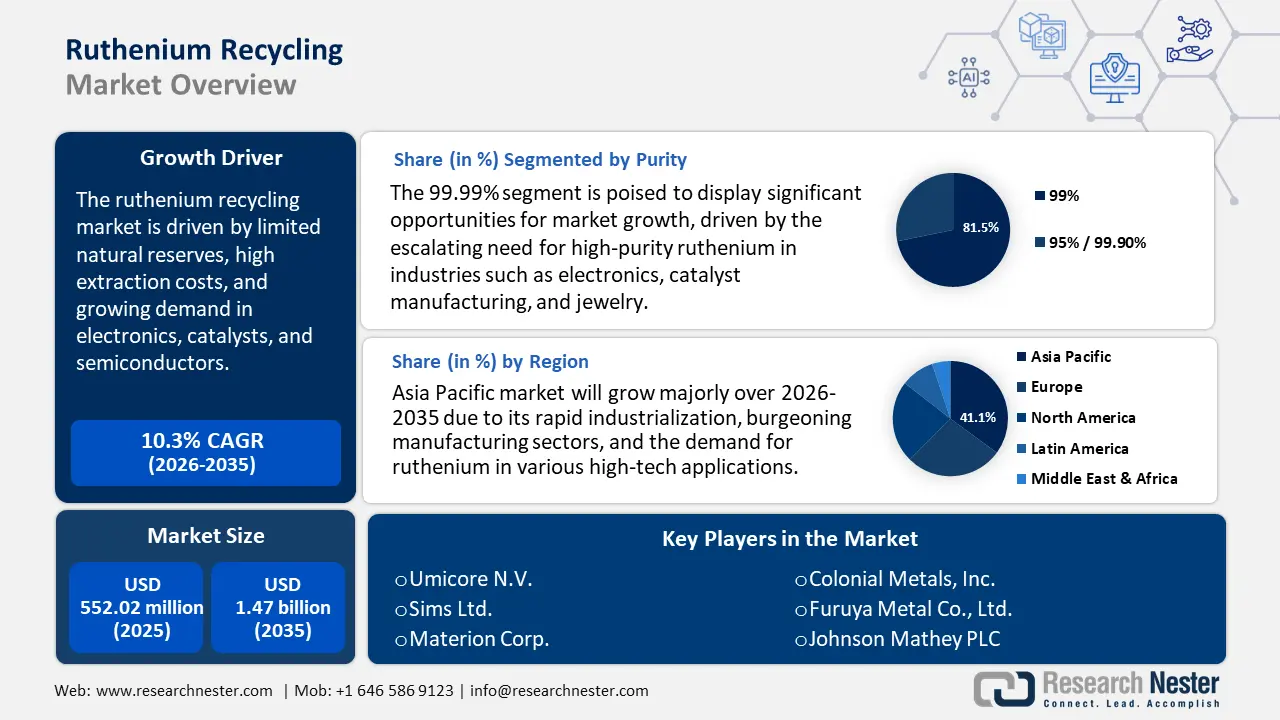
The ruthenium recycling market is highly driven by limited natural reserves, high extraction costs, and growing demand in electronics, catalysts, and semiconductors. Environmental concerns, supply chain risks, and the push for sustainable practices further encourage industries to adopt recycling as a reliable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly alternative to primary ruthenium sourcing. Ruthenium, a rare and shiny metal belonging to the platinum group, has attracted considerable interest because of its remarkable resistance to heat and its catalytic characteristics. Given its limited availability from traditional mining, primarily in South Africa, industries are focusing on recycling as a sustainable and economically viable alternative to meet the rising needs.
Companies are progressively acknowledging the advantages of recycling ruthenium, particularly in catalyst-related uses. This approach not only aligns with eco-friendly practices but also presents a lucrative opportunity for cost reduction, waste minimization, and sustainable growth. By recovering ruthenium from spent catalysts and other industrial residues, companies can minimize reliance on mining, mitigate supply chain risks, and contribute to a circular economy.
One of the notable instances is Umicore, a global materials technology company headquartered in Belgium. Umicore has developed advanced recycling processes to recover PGMs, including ruthenium, from spent industrial catalyst. Their refining technology ensures efficient and environmentally responsible reclamation of valuable metals, supporting industries in achieving sustainability goals.
By processing materials such as spent automotive and industrial catalysts, Umicore not only recovers precious metals but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with primary metal extraction. As the need for ruthenium continues to grow, embracing recycling from discarded products becomes a sensible and strategic choice. It enables industries to secure a stable supply of this critical metal while promoting environmental stewardship and economic efficiency.
Key Ruthenium Recycling Market Insights Summary:
Regional Highlights:
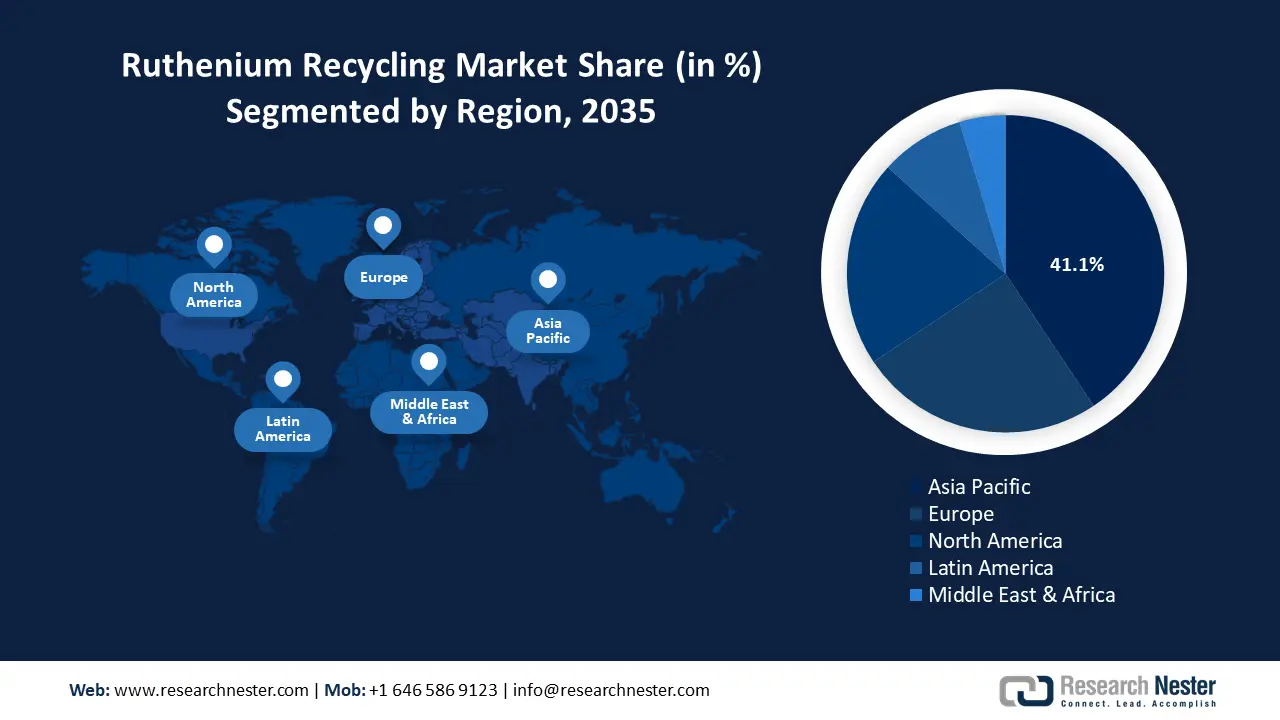
- Asia Pacific leads the Ruthenium Recycling Market with a 41.1% share, fueled by rapid industrialization, burgeoning manufacturing sectors, and escalating demand in China and India, ensuring robust growth through 2026–2035.
Segment Insights:
- The 99.99% Purity segment is projected to hold 81.5% market share by 2035, driven by the escalating need for high-purity ruthenium in electronics, catalyst manufacturing, and jewelry.
- The 99.99% Purity segment is anticipated to capture the largest share by 2035, fueled by continuous demand for high-purity ruthenium in premium industrial applications.
Key Growth Trends:
- Rising need for high-tech applications
- Economic viability
Major Challenges:
- Complex recovery process
- Collection and segregation issues
- Key Players: Heraeus Holding GmbH, Umicore N.V., and Johnson Matthey PLC.
Global Ruthenium Recycling Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 552.02 million
- 2026 Market Size: USD 603.19 million
- Projected Market Size: USD 1.47 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 10.3% CAGR (2026-2035)
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: Asia Pacific (41.1% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Asia Pacific
- Dominating Countries: China, Japan, United States, Germany, South Korea
- Emerging Countries: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan
Last updated on : 12 August, 2025
Ruthenium Recycling Market Growth Drivers and Challenges:
Growth Drivers
-
Rising need for high-tech applications: The escalating need for ruthenium in high-tech applications such as semiconductors, electronics, and chemical catalysts has intensified the demand for a consistent and affordable supply. Ruthenium’s exceptional properties, including high thermal stability, low resistivity, and resistance to electromigration, make it an ideal material for enhanced technologies. In the semiconductor industry, especially ruthenium is emerging as a superior alternative to copper for creating finer, thinner, and more conductive interconnects in logic chips.
As device architecture shrinks, copper interconnects face challenges like increased resistivity and electromigration, where ruthenium offers the potential for barrierless interconnects, simplifying manufacturing processes and enhancing device performance. A notable instance is Heraeus, a global technology company headquartered in Germany, which has developed a range of volatile ruthenium precursors tailored for atomic layer deposition (ALD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes in semiconductor fabrication. These precursors facilitate the deposition of high-purity ruthenium films, enabling the production of next-generation microchips with improved performance and reliability.
Heraeus’s innovations in ruthenium chemistry are instrumental in addressing the industry’s scaling challenges and meeting the growing need for advanced electronic devices. As the global push for miniaturization and enhanced performance in electronic devices continues, the strategic importance of ruthenium in high-tech applications is expected to rise, underscoring the need for sustainable sourcing and efficient recycling practices to ensure a stable supply chain. - Economic viability: Recycling ruthenium from end-of-life products and industrial scrap has become an economically viable strategy to mitigate production costs and reduce dependency on volatile raw material markets. Given the limited availability of ruthenium and its critical applications in electronics, catalysis, and renewable energy technologies, recycling not only ensures a stable supply but also aligns with sustainable practices.
A pertinent instance is Rubamin Pvt. Ltd., an Indian company specializing in the recycling of critical metals from industrial waste. Rubamin operates a Green Recycling Complex in Gujarat, India, where it recovers valuable metals from spent catalysts and other industrial residues. By processing materials such as spent automotive and industrial catalysts, Rubamin not only recovers precious metals but also reduces the environmental impact associated with primary metal extraction. This strategy allows Rubamin to provide high-purity metal chemicals to catalyst manufacturers worldwide, showcasing the economic and environmental advantages of recycling.
As the global need for ruthenium continues to rise, driven by its critical applications in electronics, catalysis, and renewable energy technologies, the role of recycling becomes increasingly vital. By investing in and adopting efficient recycling practices, industries can not only mitigate supply risks but also contribute to environmental conservation and economic resilience.
Challenges
- Complex recovery process: Ruthenium is typically found in trace amounts with complex industrial materials, such as spent catalysts, electronics components, and chemical residues. Its dispersion across various substrates and the presence of other metals or contaminants make the recovery process highly intricate. Enhanced separation and refining technologies are required to isolate and purify ruthenium without significant material loss, which can be technically demanding and capital-intensive. Additionally, the chemical behavior of ruthenium, especially its tendency to form volatile compounds, adds further complexity to the recycling process. These challenges collectively increase operational costs and limit widespread adoption of ruthenium recycling practices.
- Collection and segregation issues: Efficient recycling of ruthenium relies heavily on the effective collection and segregation of ruthenium-containing end-of-life products. However, this process is often hindered by a lack of awareness among consumers and industries about the presence and value of ruthenium in various components such as alloys, electronic devices, and catalysts. Furthermore, the absence of standardized procedures for identifying, sorting, and handling these materials complicates recovery efforts. In many cases, ruthenium-bearing waste is either discarded or processed with general scrap, leading to material loss. Addressing these issues requires better education, regulatory support, and the development of dedicated recycling and sorting infrastructure.
Ruthenium Recycling Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
10.3% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 552.02 million |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 1.47 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Ruthenium Recycling Market Segmentation:
Purity (99.99%, and 99.95% / 99.90%)
The 99.99% purity segment dominated the global ruthenium recycling market, capturing a substantial 81.5% market share in 2035. This dominance is primarily driven by the escalating need for high-purity ruthenium in industries such as electronics, catalyst manufacturing, and jewelry. High-purity ruthenium is essential in these sectors to ensure optimal performance and quality, especially in applications like semiconductors, where even minimal impurities can significantly impact functionality.
A notable instance is Tanaka Kikinzoku Kogyo K.K., a Japanese company specializing in precious metals. Tanaka has developed a two-stage Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) process using liquid ruthenium precursors, enabling the formation of high-quality ruthenium films. This innovation underscores the industry’s emphasis on ultra-high-purity ruthenium for advanced technological applications. The segment featuring 99.99% purity is expected to capture the largest ruthenium recycling market share throughout the forecast period, indicating a continuous demand for high-purity ruthenium in numerous premium industrial applications. On the other hand, the 99.95% / 99.90% ruthenium purity segment highly used in less demanding industrial applications, this segment offers cost-effective alternatives for sectors not requiring ultra-high purity.
Application (Electrical & Electronics, Chemical Catalysis, Electrochemical, and Other Applications)
The chemical catalysis segment holds a dominant position in the ruthenium recycling market. This prominence is attributed to ruthenium’s extensive use as a catalyst in various industrial processes, including petrochemical refining, pharmaceutical synthesis, and fine chemical production.
Ruthenium catalysts are renowned for their high selectivity and efficiency, enabling precise control over complex chemical reactions while operating under milder conditions, which leads to energy savings and enhanced process efficiency. One prominent example is Johnson Matthey, a worldwide frontrunner in sustainable technologies, which provides a variety of ruthenium-based catalysts designed for various applications. Their product portfolio includes biocatalysts, enhanced homogenous catalysts, chemocatalysts, and heterogenous catalysts for small molecule applications like the pharmaceutical market. These catalysts are designed to deliver high performance in terms of activity and selectivity, thereby meeting the stringent requirements of modern chemical manufacturing.
The rising need for high-purity ruthenium catalysts, along with progress in recycling technologies, highlights the essential contribution of the chemical catalysis sector to the expansion of the ruthenium recycling market.
Our in-depth analysis of the global ruthenium recycling market includes the following segments:
|
Purity |
|
|
Application |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Ruthenium Recycling Market Regional Analysis:
APAC Market Statistics
In 2035, the Asia Pacific is expected to emerge as the dominant force in the global ruthenium recycling market, commanding a substantial 41.1% share of total revenue. This dominance is due to its rapid industrialization, burgeoning manufacturing sectors, and the escalating demand for ruthenium in various high-tech applications, including electronics, catalysis, and renewable energy technologies in China and India. The collaboration between BASF and Heraeus to establish BASF HERAEUS (China) Metal Resource Co., Ltd. exemplifies China's commitment to enhancing its precious metal recycling capabilities. This joint venture focuses on recovering platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts, supporting China’s circular economy initiatives, and reducing reliance on imported raw materials.
India's advancement is illustrated by firms like Ravindra Heraeus, which has established the country's first pyrometallurgical smelter focused on the recycling of precious metal catalysts in Udaipur. This facility enables the efficient recovery of platinum group metals from various industrial catalysts, catering to the growing domestic demand. Companies like Onyx Metals and Adi MetChem exemplify the nation’s commitment to enhancing precious metal recycling capabilities. Onyx Metals, located in Mumbai, focuses on the eco-friendly extraction and refining of precious metals, such as ruthenium, sourced from industrial waste and scrap materials. Similarly, Adi MetChem offers comprehensive precious metal refining services, utilizing high-tech facilities to efficiently recycle spent catalysts and refine metals like ruthenium to meet stringent industry standards. These initiatives underscore the pivotal roles of China and India in propelling the APAC’s leadership in the ruthenium recycling market, aligning with global sustainability and resource-efficient goals.
Europe Analysis
Europe is expected to hold the second position in the global ruthenium recycling market during the forecast period. This strong market presence is underpinned by substantial investments in advanced recycling technologies across key European nations, notably in the UK and Germany. Germany plays a pivotal role in the European ruthenium recycling market, driven by its advanced industrial infrastructure and commitment to sustainable practices.
On the other hand, in the UK, Altilium, an electric vehicle battery recycling firm, has attracted significant investments, including a USD 5 million infusion from Japanese trading company Marubeni. This funding aims to scale up Altilium’s operations, enhancing the recycling of valuable battery minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are critical for various applications, including those involving ruthenium. Altilium’s expansion plans include recycling approximately 24,000 EV battery packs annually by 2026, with ambitions to increase this number to 150,000 by 2030. These companies' investments in cutting-edge recycling technologies bolster Europe’s position as a leader in the ruthenium recycling sector.
Key Ruthenium Recycling Market Players:
- BASF SE
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- Heraeus Holding GmbH
- Umicore N.V.
- Johnson Matthey PLC
- Dowa Holdings Co. Ltd.
- TANAKA Precious Metals
- Sims Ltd.
- Materion Corp.
- Furuya Metal Co., Ltd.
- Shanxi Kaida Chemical Engineering Co., Ltd
- Colonial Metals, Inc.
- Changshu Changhong Precious Metal Co., Ltd
Key players use advanced hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical technologies to efficiently extract ruthenium from spent catalysts and electronic waste. Their focus on selective operations enables them to lead the ruthenium recycling market with high-purity yields and lower environmental impact.
Recent Developments
- In August 2023, the team at TU Freiberg created a recycling process aimed at extracting precious metals from electrolytes, emphasizing hydrometallurgical techniques. This procedure involves dissolving the catalyst substance in a water-based solution and subsequently recovering it as a solid, which may be in the form of either a salt or a metal, achieving a high level of purity.
- In May 2023, Heraeus Precious Metals, a prominent provider of precious metal products and one of the foremost recyclers of platinum group metals, announced an expansion of its recycling capabilities at its headquarters in Hanau, Germany, backed by a 35-million-euro investment
- Report ID: 7613
- Published Date: Aug 12, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Ruthenium Recycling Market Report Scope
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




