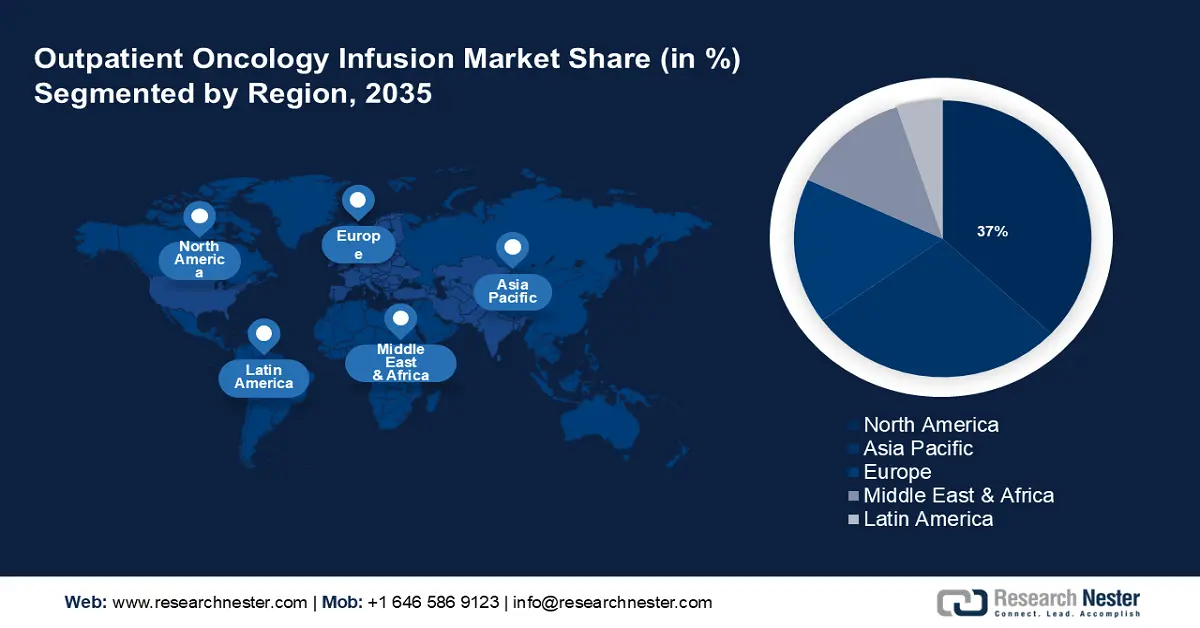
Outpatient Oncology Infusion Market Regional Analysis:
North America Market Insights
North America industry is likely to dominate majority revenue share of 37% by 2035. The market growth in the region is expected on account of the expanding outpatient care industry and the presence of sophisticated healthcare infrastructure. As a result, outpatient facilities and services are growing in the region, which has enabled medical centers to lower the number of visits and reduce healthcare costs for cancer patients. For instance, the North America outpatient care landscape is anticipated to expand by around 4% between 2024 and 2029.
Additionally, in the U.S., the outpatient oncology infusion market is constantly changing owing to growing healthcare spending. With increased funds, researchers can focus on innovation, and offer more precise and effective options for patients. A 2024 report published by the American Medical Association stated that healthcare spending in the U.S. increased by 4.1% in 2022.
Furthermore, in Canada, there are currently more IV infusion therapies approved than ever before, and several more are being considered for approval in the future, which may propel improvements in cancer treatment and aid in the market's expansion.
APAC Market Insights
Asia Pacific will encounter tremendous growth in the outpatient oncology infusion market owing to the increasing adoption of telemedicine. Through 2024, telehealth adoption is anticipated to soar in the region, enabling healthcare professionals to democratize the delivery of outpatient oncology infusion services easily in distant areas. Several countries are expected to reach telehealth adoption rates of over 70 percent by 2024, with China leading the way at 76 percent. Besides this, regional governments have pledged to create legislation and carry out initiatives to enhance cancer care and treatment accessibility.
Telemedicine adoption in Japan has accelerated in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and a push to improve healthcare accessibility. The government and healthcare organizations have increasingly recognized the value of telemedicine, particularly in the context of chronic disease management.
The government of China launched the National Cancer Control Program to reduce the cancer burden through early detection, treatment, and prevention. This program includes efforts to enhance outpatient care and support for cancer patients.