Microbial Cellulose Market Outlook:
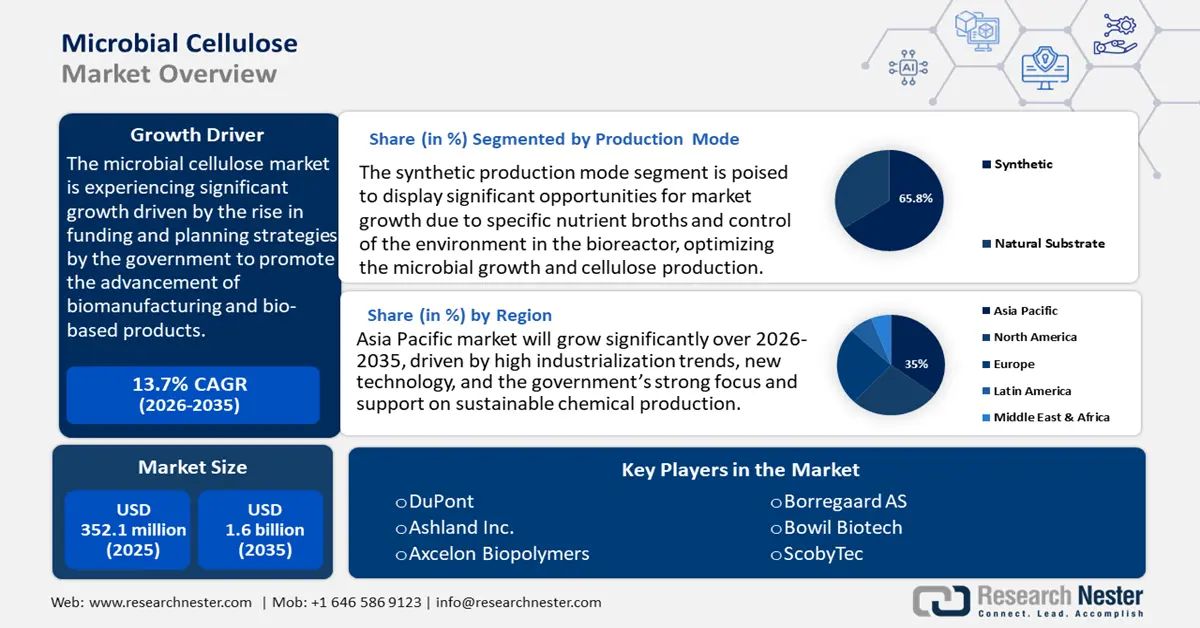
Microbial Cellulose Market size was valued at USD 352.1 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1.6 billion by the end of 2035, rising at a CAGR of 13.7% during the forecast period, i.e., 2026-2035. In 2026, the industry size of microbial cellulose is assessed at USD 399 million.
The microbial cellulose market is projected to grow significantly, primarily driven by the rise in funding and planning strategies by the government to promote the advancement of biomanufacturing and bio-based products. The U.S. federal agencies have invested heavily in scaling sustainable biotechnologies such as microbial cellulose. The U.S. Department of Energy is investing millions to advance biobased chemical production and scale up integrated biorefineries, including USD 120 million to support biotechnology commercialization and USD 220 million for biomanufacturing R&D and scale-up efforts. These initiatives aim to accelerate renewable chemical innovations, such as microbial cellulose manufacture, and reduce carbon emissions in key sectors.
In addition to that, the U.S. Department of Agriculture directed USD 8 million in 2024 as an investment in biorefining, biomanufacturing projects through its National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA), which promotes more biomaterial commercialization and industrial scaling. The BioMADE Manufacturing Innovation Institute, operated by the Department of Defense, was allotted USD 450 million to create an ability in bio-industrial manufacturing, such as assistance in procuring sustainable feed stocks, including fermentation technology that is vital in the production of microbial cellulose.
Within the context of microbial cellulose supply chain development, the federal agencies have also implemented prioritization on creating resilient logistics and sourcing schemes toward reducing bottlenecks in raw materials and enabling their manufacturing operations to be efficient and scalable. In a recently published 2023-billion-ton Report, the U.S. Department of Energy notes that there is substantial progress being made using agricultural residues as key precursors to bio-based production, and that more than 1 billion dry tons of biomass can be sustainably sourced across the United States annually by 2030, well beyond current manufacturing demands and able to provide secure biomass feedstocks to microbial cellulose facilities. Such logistics advances enable their producers to decrease imports and make input prices more stable, and achieve more reliable assembly line activity that biomanufacturing thereafter. The DOE’s collaborative Sustainable Aviation Fuel-Grand Challenge initiative, which invests $80 million in developing supply chains for transportation fuels and chemicals derived from biomass and waste resources. This program specifically aims to create robust, domestic supply chains for renewable bio-based materials, enhancing production speed and resilience against global disruptions.
Key Microbial Cellulose Market Insights Summary:
Regional Insights:
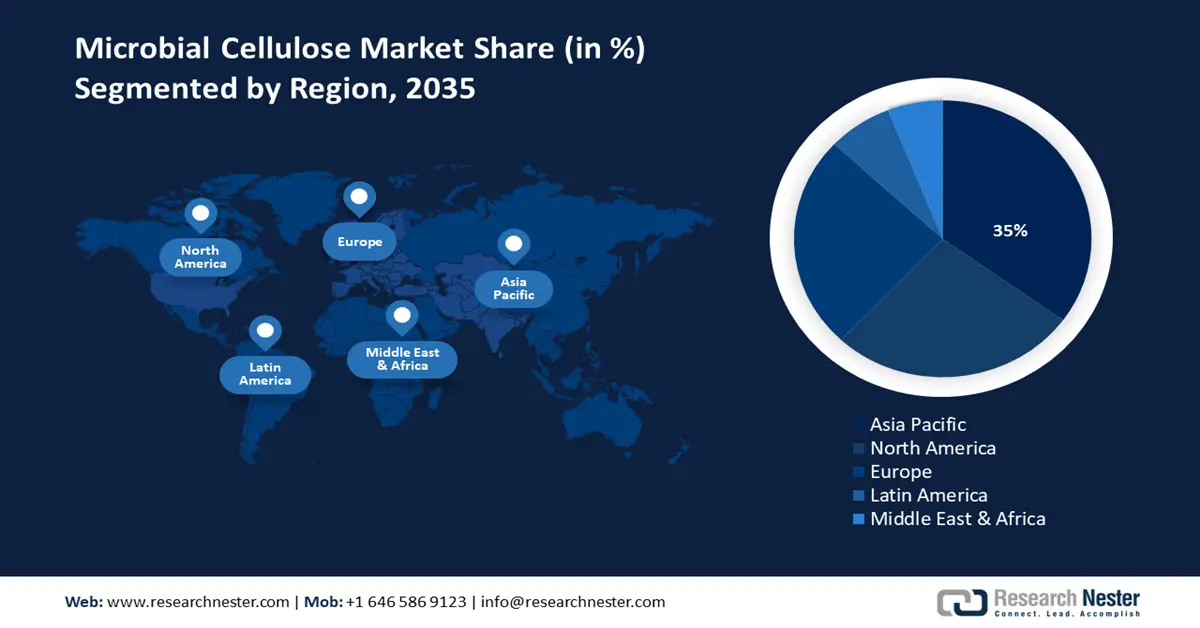
- By 2035, Asia Pacific is projected to command a 35% revenue share in the microbial cellulose market, underpinned by rapid industrialization, expanding technological capabilities, and strong governmental backing for sustainable chemical production.
- North America is forecast to secure a 27% revenue share during 2026–2035, supported by rising preferences for biodegradable materials across industries and reinforced by EPA initiatives toward greener chemical technologies.
Segment Insights:
- The synthetic production mode segment is expected to hold a dominant 65.8% share from 2026 to 2035 in the microbial cellulose market, bolstered by tightly controlled bioreactor environments that enhance yields and process consistency through bio-process optimization advancements.
- The Acetobacter genus segment is projected to grow at 42.4% through 2035, powered by productivity gains from adaptive evolution and carbon-source optimization that heighten cellulose output and strengthen its scalability in commercial applications.
Key Growth Trends:
- Regulatory stringency and compliance costs
- Innovation in chemical recycling
Major Challenges:
- Stringent environmental regulations
- Rising costs of compliance
Key Players: Ashland Inc., Axcelon Biopolymers, Borregaard AS, Bowil Biotech, ScobyTec, Polybion, Bioweg, Nanollose Ltd., HNB BIO CO., LTD, Maple Biotech.
Global Microbial Cellulose Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 352.1 million
- 2026 Market Size: USD 399 million
- Projected Market Size: USD 1.6 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 13.7%
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: Asia Pacific (35% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Europe
- Dominating Countries: United States, China, Japan, Germany, South Korea
- Emerging Countries: India, Australia, Brazil, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom
Last updated on : 21 August, 2025
Microbial Cellulose Market - Growth Drivers and Challenges
Growth Drivers
- Regulatory stringency and compliance costs: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has taken several actions in the last few years that have intensely increased the cost of compliance to manufacturers of chemicals, including recently proposed new regulations covering persistent, bio accumulative and toxic (PBT) substances such as PIP (3:1) and expanded TSCA reporting for PFAS. Implementation and reporting are estimated to cost industry-wide more than $800 million in 2023, and individual companies may incur a significant increase in compliance costs based on estimates of cost analysts in the microbial cellulose market. Such regulatory changes are likely to require microbial cellulose manufacturers to establish improvements in their tracking, disclosure, and supply chain standards, which will affect operating expenses and product costs directly.
- Innovation in chemical recycling: Results of studies carried out in the UK microbial cellulose market and the EU have shown the possibility of recycling polycotton fiber using chemical recycling into microbial cellulose, creating new circular bio-based material supply chains. Pilot projects have already shown positive extraction and conversion, and as much as 2kg of bacterial cellulose has been produced in a month using recycled fibers. This invention not only prevents the waste from entering the landfill but also promotes a renewable supply of raw materials to manufacture microbial cellulose, which appeals to environmentally conscious customers and helps increase competitiveness in the global microbial cellulose markets.
- Bio-based chemical trade expositions: Federal assistance and partnerships in the chemical industry are catalyzing the growth of bio-based chemical sales, including microbial cellulose. The USDA Science and Research Strategy (2023-2026) outlines investments in biomanufacturing projects aimed at advancing the commercialization of microbial cellulose. These initiatives focus on increasing production capacity and improving access to international microbial cellulose market, supporting expanded trade opportunities for U.S. biobased products. In turn, this growth is manifested in the appearance of new export outlets and increased volumes of shipments, which will be established with the implementation of improved bioprocessing infrastructure in North America. The above strategies enhance the stability of supplies and promote the increase of microbial cellulose products in international microbial cellulose market.
Microbial Cellulose Production
The yield of bacterial cellulose production is highly dependent on the choice of growth medium, with optimized nutrient formulations significantly improving output efficiency. The traditional Hestrin-Schramm (HS) medium remains the industry benchmark, although its high cost limits large-scale deployment. Alternative low-cost substrates such as agricultural byproducts, fruit extracts, and industrial waste streams have demonstrated competitive yields while reducing raw material expenses. For commercial producers, this presents opportunities to balance performance with cost efficiency, enabling scalable and sustainable manufacturing pathways for bacterial cellulose across various applications, including packaging, biomedical, and specialty materials.
Yield of Bacterial Cellulose with the Variation of Bacterial Strains, Culture Medium, and Cultivation Methods
|
Medium |
Bacterial Strain |
Incubation Days |
Yield of BC (g/L) |
|
Glycerol |
Gluconacetobacter sp. RKY5 |
6 |
4.59 a, 5.63 b |
|
Glucose yeast extract broth |
Acetobacter xylinum K086 |
7 days |
0.14-0.39 a |
|
Glucose yeast extract broth |
Acetobacter xylinum K975 |
7 days |
1.11-1.55 a |
|
Glucose yeast extract broth |
Acetobacter xylinum K428 |
7 days |
0.09-0.22 a |
|
Glucose yeast extract broth |
Acetobacter xylinum K1011 |
7 days |
0.57-1.46 a |
|
Glucose yeast extract broth |
Acetobacter xylinum KX |
7 days |
1.14-1.84 a |
|
Glycerol |
Acetobacter sp. V6 |
7 days |
4.98 b |
|
Molasse |
Komagataeibacter sucrofernentans H110, Komagataeibacter hansenii C110 |
14 days |
8.2 ± 0.2 a, 8.1 ± 0.2 a |
|
Stillage |
Komagataeibacter sucrofernentans H110, Komagataeibacter hansenii C110 |
14 days |
9.5 ± 0.1 a, 9.2 ± 0.1 a |
|
Citrus waste solution |
Gluconacetobacter intermedius CIs26 |
8 days |
7.2 a |
|
HS media |
Gluconacetobacter intermedius CIs26 |
8 days |
2.1 a |
|
Citrus waste modified HS |
Gluconacetobacter intermedius CIs26 |
8 days |
5.7 a |
|
Glucose |
Gluconacetobacter hansenii |
2 |
1.33 b |
|
Glucose (modified HS Media) |
Gluconacetobacter hansenii |
14 |
14.72 a |
|
Mannitol (modified HS media) |
Gluconacetobacter hansenii |
20 |
14.72 a |
|
Pineapple peel juice |
Gluconacetobacterswingsii |
13 |
2.8 a |
a: static cultivation, b: agitated cultivation
Challenges
- Stringent environmental regulations: In the U.S., the manufacturing companies of microbial cellulose must comply with the rules of the EPA relating to air emissions, hazardous wastes, and chemicals. EPA has issued 770 Notices of Violation to chemical firms since 2023 alone for non-compliance with air quality standards, and these firms are incurring huge investments to have pollution abatement technologies and upgrade the process. These expenses may incur a significant share of the entire operating expenses among SME producers, and usually lead to inefficient arrival of innovative merchandise to the microbial cellulose market. Another impediment to scaling production of microbial cellulose is the requirement by EPA enforcement that companies significantly redefine safety guidelines and procedures, which also makes the process of scaling a cost-prohibitive reason not to scale.
- Rising costs of compliance: In a 2024 survey by the American Chemistry Council, 86% of U.S. chemical manufacturers experienced increased, escalating regulatory requirements, such as documentation, traceability, and safety, over the last three years. Compliance costs in chemical manufacturing, including production of new bio-based products like microbial cellulose, can represent a significant portion of total expenses—often reducing profitability and discouraging adoption of innovative technologies. This increased compliance is leading to slower research and development, a long product launch period, and limited products being introduced that only generate high-margin goods.
Microbial Cellulose Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Year |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
13.7% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 352.1 million |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 1.6 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Microbial Cellulose Market Segmentation:
Production Mode Segment Analysis
The synthetic production mode segment is expected to grow at the largest microbial cellulose market share of 65.8% from 2026 to 2035, attributed to specific nutrient broths and control of the environment in the bioreactor, which ideally optimizes the microbial growth and cellulose production. Cellulose yields of up to 26.4 g/L using high-density fermentation trials are much greater than is achieved using natural substrates, because the amount of pH, oxygen transfer, and nutrient addition can each be carefully controlled. This also minimizes batch-to-batch variability and risk of contamination and enhances the compliance of medical, food, and cosmetic applications with repeatability and quality requirements. Funding and industry investments in bio-process optimization, and the fields of synthetic biology, are augmenting the speed at which adoption of cost-efficient commercial-scale Microbial cellulose production is sparked.
Further, standardized nutrient broth formulations for microbial cellulose production typically include 2% glucose, citric acid, yeast extract, peptone, and mineral salts, enabling strains such as Komagataeibacter hansenii to achieve yields up to 14.72g/L using modified HS media over 14 days. This uniformity lowers batch-to-batch variability and avoids contamination risks, and it is suitable in industrial applications in food and medical fields, since it is scalable. Meanwhile, high-tech growth conditions in bioreactor-based production, including more sophisticated temperature, aeration, and mixing control, are used to produce optimal amounts of microbial cellulose, and have recently been reported that agitated bioreactor systems, optimizing factors like aeration and agitation speed (100-300rpm), can deliver yields between 4.59g/L and 11.46g/L depending on strain and culturing method. Alternative low-cost substrates—such as citrus waste, molasses, and pineapple peel juice- have yielded between 2.8g/L and 9.5g/L, while optimized oxygen delivery in fed-batch processes further enhances productivity for industrial applications. Combined, the strategies form a strong foundation for the scale-up of high-quality large-scale production of microbial cellulose with support of regulatory approval and investment by industry.
Type Segment Analysis
The Acetobacter genus segment in the microbial cellulose market is expected to grow at a significant rate of 42.4% during the projected years. Komagataeibacter xylinus, a component of the Acetobacter genus, is usually the major microbial agent that is utilized in the manufacturing of cellulose bacterium in industrial and laboratory conditions. As per the recent study, using methods of adaptive laboratory evolution and optimized carbon sources, such as mannitol, K. xylinus may attain up to 38% higher cellulose yields over and above product quality. This productivity development is essential in the scaling up microbial cellulose production process and is expected to grow at a substantial rate market share by 2035. Its cellulose exhibits high mechanical strength, crystallinity, and biocompatibility and increasing its demand in the fields of biomedical, textile, and packaging materials, enhancing its dominance in the commercial sphere. Ongoing experimentation and metabolic engineering work should help further increase its level of efficiency and sustainability.
The most productive species in the Acetobacter segment in the microbial cellulose market are Komagataeibacter xylinus and Acetobacter aceti. Komagataeibacter xylinus cultivated in a magnetically assisted external-loop airlift bioreactor (EL-ALB) achieved bacterial cellulose yields of 7.26 g/L dry mass, with high and stable metabolic activity and cellular density during repeated batch fermentation. The resulting cellulose consistently displayed strong water-related properties, a nanofibrillar structure with an average diameter of about 53.8 nm, a total crystallinity index around 1.61, and mechanical strength with an average tensile strength of 2.41 MPa and Young’s modulus of 11.75 MPa, attributes that support its use in tissue engineering, wound healing, and drug delivery.
Although traditionally considered in the production of vinegar, A. aceti also has the benefit of a strong cellulose-producing ability, with standard fermentation protocols yielding as high as 6.0 g/L, especially when oxygenation and nutrient availability are effectively regulated. Together, these two strains provide the majority of the world microbial cellulose market on Acetobacter-based microbial cellulose, contributing to the strong demand in biomedical and advanced material industries and the continued advances in fermentation and in the use of low-cost substrates.
Application Segment Analysis
The medical and biomedical applications segment in the microbial cellulose market is anticipated to grow at a steady pace over the forecast years, due to its excellent performance properties. Bacterial cellulose membranes have good tensile strength under moist conditions, good wound moisture retention capacity, and low skin irritation potential. The properties allow their application in sophisticated wound dressings, skin graft surrogates, and tissue engineering scaffolds. New developments in the production of antimicrobial bacterial cellulose wound dressings have continued to widen the functional scope, thus minimizing the risk of infection during clinical application. Notable research grants by the government, regular approvals in regulatory status, and expanding microbial cellulose market demand for sustainable biopolymers in healthcare are contributing strongly to the growth of this segment. New opportunities are still emerging as far as the future of biofunctionalization and incorporation of composite materials is concerned.
Our in-depth analysis of the microbial cellulose market includes the following segments:
|
Segment |
Subsegment |
|
Type |
|
|
Production Mode
|
|
|
Application |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Microbial Cellulose Market - Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific Market Insights
The Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the microbial cellulose market, growing at a revenue share of 35% by the year 2035 due to high industrialization trends, new technology, and the government’s strong focus and support on sustainable chemical production. The microbial cellulose market growth in the region is spurred by the growing demand in the various sectors such as machine packing, healthcare, and electronics sectors, where green and biodegradable package materials are in priority. There are regulatory frameworks that drive the use of bio-based chemicals and circular economy projects across the Asia Pacific region, which are backed by aggressive research, development, and manufacturing infrastructure investments. For example, India’s Department of Biotechnology (DBT) “Bio-RIDE” scheme has an approved outlay of ₹9,197 crore (approximately USD1.1 billion) for 2021-2026 to support biomanufacturing, circular economy, and bio-based chemicals, including grant funding, infrastructure, startups, and commercialization incentives.
Policies of environmental sustainability and green chemistry have triggered innovations in the use of microbial cellulose and the commercialization of the same. Moreover, cooperations in the development of technologies and scale-up activities occur faster in private-public and regional collaborations. The increase in consumer awareness regarding environmental emissions and more strict procedures addressing the problems of plastic and chemical waste also supports the growth of the microbial cellulose market. All these are what make the region the fastest-growing and biggest microbial cellulose market segment in the world, with innovation, policy framework, and a wide range of end-use industries dedicated to sustainable growth.
The China microbial cellulose market is growing at a very fast pace, backed by the rapid expansion of the country’s bioeconomy, supported by strong policy frameworks from the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and stringent sustainability regulations enforced by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE). The sector is a major focus of government strategy, with microbial cellulose market valuation projected to reach 22 trillion yuan (approximately $3.3 trillion) by 2025. This growth is underpinned by comprehensive regulatory support and large-scale investments in sustainable chemical manufacturing and biomaterials. With the regulatory support and funding structure, there has been widespread industry approval in terms of packaging, health care, and the specialty chemicals sector, entrenching China as the leader of the Asia Pacific microbial cellulose market.
India’s microbial cellulose market is expected to rise at the largest CAGR over the projected years, driven by the strategic policy measures by the Department of Science & Technology (DST) and specific investments by the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers. The country has seen substantial growth in the microbial cellulose market. For instance, the Department of Science & Technology (DST), strategic policy initiatives such as CERI include funding India-centric technology deployment testbeds for carbon capture, utilization, and conversion technologies, such as the coal-to-methanol pilot at IIT Delhi-Thermax Ltd, and CO₂-to-Dimethyl Ether facility at CSIR-IICT Hyderabad, BHEL, supporting alternative fuels and sustainable chemical manufacturing.
Moreover, the sponsorship programs of the Indian government have led to wide-reaching ads of green chemicals/processes in the chemical industry, which promotes commercialization beyond its typical industries. The assistance of such initiatives is by policy, including the Petroleum, Chemicals and Petrochemicals Investment Regions (PCPIR) scheme and the Chemicals (Management and Safety) Rules that seek to promote sustainable manufacturing and cleaner production technologies. The microbial cellulose market size in India was USD 447.25 million in 2023 and is anticipated to reach USD 1,809.51 million by 2030. The imports with HSN code 3907 had a total net forex deficit of USD 1,502.40 million during April 2023 to January 2024, which indicated an increasing domestic demand and investments. The government promotes this sector through tax reliefs, grants, and subsidies as part of bio-manufacturing initiatives announced in the Interim Budget Speech 2024.
North America Market Insights
The North America microbial cellulose market is expected to witness a steady rise with a 27% revenue share over the projected years from 2026 to 2035, as the demand for biodegradable and sustainable materials in many industries, including healthcare, packaging, and specialty chemicals, is seeing a rise. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are more interested in environmental protection and assist in the advancement of green chemical technologies. The FY 2023 Budget demonstrates the EPA’s sustainability efforts with its overall spending of USD 11.881 billion on environmental and health programs, with separate allocation on grants to reduce methane emissions, as well as the Diesel Emissions Reduction Act program with USD 100 million and USD 150 million, respectively.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) collaboration with TAPPI and industry partners, focuses on measurement needs for cellulose nanomaterials, developing standard test methods, and environmental health and safety studies, reflecting active support for standardized, safe, and scalable production methods for bio-based materials such as microbial cellulose. These developments facilitate consistent, high-quality manufacturing and accelerate commercialization in the microbial cellulose sector. Moreover, EPA’s Green Chemistry Challenge Awards program has recognized 133 winning technologies since its beginning, which together have eliminated 830 million pounds of hazardous chemicals and solvents annually, resulting in significant reductions in hazardous waste and supporting sustainable chemical practices at the regional level. The program facilitates the adoption of innovative, sustainable chemical processes across the industry. These regulatory systems, supplemented by the investments made in the private sector, contribute to the degree of maturity present in the microbial cellulose market and allow higher adoption of microbial cellulose in North America.
The U.S. microbial cellulose market is expected to lead the North American microbial cellulose market, attributed to the increased need for sustainable cellulose-based material in medical applications, smart packaging, and wound care applications, fueled by a strong research and innovation-driven economy. The EPA used FY 2023 funding of USD 100 million to fund methane reduction and clean chemical manufacturing grants to further demonstrate its dedication to green chemical processing. According to the American Chemistry Council's 2023 Guide to the Business of Chemistry, the U.S. chemical industry invested USD 13.4 billion in research and development in 2022, focusing on new sustainable materials and processes. Furthermore, USD 26 billion was spent on new capital projects in 2022, much of which targeted sustainability improvements, highlighting comprehensive industry innovation tied to sustainability goals, including reductions in GHG emissions, energy use, and the adoption of innovative sustainable solutions.
The microbial cellulose market in Canada is stimulated by governmental grants to other bioproducts and the national sustainability policies. Budget 2023 invested nearly CAD 1.5 billion in clean technology innovation in Canada, with an emphasis on the clean fuels fund, which will run until 2030 in an attempt to increase production of sustainable fuels such as biofuels and hydrogen. In another policy act, it also provided a 30% refundable tax credit to increase clean technology production by a special emphasis on producing renewable energy and using cellulose-based bio-materials. The budget focuses on federal investment opportunities in research and commercialization for the further development of biomaterials and the clean economy. Toronto and Vancouver have very high biotech cluster potentials that support R&D interactions and microbial cellulose commercialization in the medical, cosmetics, and packaging sectors.
The chemical industry in Canada in the year 2022 made a major contribution of manufacturing shipment of 72.7 billion to the national economy, direct jobs of 90,800 individuals, and 454,000 jobs overall. It was a year in which interest in the low-carbon and bio-based chemistry investment was unprecedented, and there were more than 20 big low-carbon projects proposed in Canada. Switching to the new ones, innovative, sustainable, and bio-based, is pointed out as the trend toward growth and competitiveness in the future.
Europe Market Insights
The microbial cellulose market in Europe is anticipated to grow at a rate of 31% from 2026 to 2035, due to the strong level of chemical production within the class of chemicals, as well as the level of policy encouragement in bio-based innovation within the developed microbial cellulose market. In 2023, the turnover of the chemical production sector amounted to €655 billion and the €165 billion added value, including 31000 companies with 97% as SMEs within the European region. The area is also second with regard to chemical patent registration in the whole world, showing its high innovation potential. At the same time as investment in bio-based materials and biopolymers is increasing, regulation becomes a key feature of the current policies, and the current policy needs to apply greater incentives in the field of finance to make sustainable innovation more rapid.
The medical, packaging, and electronic sectors show the highest microbial cellulose market demand, and a great number of states of EU states declare a pilot project of circular bioeconomy processes. BioSolutions' research and re-use innovations are funded by industry leaders across the region. The Clean Industrial Deal of the European Commission will mobilise more than €100 billion to clean manufacturing, including significant investment in advanced chemicals, biomaterials associated with Green Deal targets. The large-scale funding, however, includes support for sustainable chemicals, bio-based materials, and deployment of clean technology in the EU. The chemical industry in Germany generated a half-yearly revenue of EUR107 billion in 2025 and saw enhanced capabilities in biomaterials and sustainable commercialization of microbial cellulose in drug production and packaging, and funding and policy measures continue to be injected into the industry to support growth and sustainability.
Key Microbial Cellulose Market Players:
- DuPont
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- Ashland Inc.
- Axcelon Biopolymers
- Borregaard AS
- Bowil Biotech
- ScobyTec
- Polybion
- Bioweg
- Nanollose Ltd.
- HNB BIO CO., LTD
- Maple Biotech
The microbial cellulose market is moderately dynamic, with leading manufacturers harnessing biotechnological innovation and local capability to dominate in the sustainable chemical solutions market. The strategies of making test investments in R&D, partnerships, and green chemistry are used by such companies as Ashland, Borregaard, Nippon Paper Industries, and Nanollose as a way of spreading their product portfolios and markets. European, US, and APAC companies are focused on applications of medical, cosmetics, and packaging, and tend to cooperate with research institutes and regulatory bodies to obtain advanced functional materials. This constant emphasis on product innovation, environmentally friendly procedures, and global supply chain optimization is expected to ensure that they remain competitive and attract growth in the microbial cellulose market.
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Birla Cellulose introduced a new cellulose-based textile solution, Liva with Antimicrobial Protection, offering long-lasting antimicrobial protection on fashion and home textile applications. The product addresses the emerging trend of sustainable and health-promoting options of fabrics, incorporating high-tech chemical levels of cellulose into its design and comfort. Within two quarters, its commercial launch led to a sharp 12 percent growth in the Birla Cellulose segment as textile producers adopted the product because of its functional and eco-friendly characteristics. At the time, Liva set new benchmarks in cellulose-derived fibers, and it was also credited with pioneering the market to adopt new, eco-friendly, bio-based technologies.
- In April 2025, Rice University and the University of Houston announced a breakthrough bacterial cellulose material biosynthesized using a dynamic biosynthesis method. The process is the first to align cellulose fibres in real time in such a way that biopolymer sheets are produced with remarkable mechanical properties-approaching 436 megapascals. The invention focuses on use in structural packaging and thermal management products, which positions the material in high demand by electronic manufacturers within North America. After its introduction, the demand in the market increased by 15%, with firms needing alternative polymers that were stronger and more sustainable in the market. The partnership drew the attention of the industry in furthering the cause of eco-friendly, high-performance cellulose technology.
- Report ID: 8012
- Published Date: Aug 21, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Microbial Cellulose Market Report Scope
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




