Genetically Modified (GMO) Food Market Outlook:
Genetically Modified (GMO) Food Market size was valued at USD 123.9 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 245.6 billion by the end of 2035, rising at a CAGR of 7.9% during the forecast period, i.e., 2026-2035. In 2026, the industry size of genetically modified food at USD 133.6 billion.

The genetically modified food market is exponentially growing on account of increasing demand for high-yield, nutrient-enriched, and pest-resistant crops. Advancements in biotechnology are encouraging the development of foods with enhanced shelf life, improved nutritional profiles, and resistance to environmental stresses. In this regard, the USDA Biotechnology Risk Assessment Grants program in December 2025 reported that it provides funding to support research on the environmental risks and management of genetically engineered organisms, which include plants, animals, insects, and microorganisms. It also reported that in FY 2024, BRAG received 33 proposals, requested USD 18.4 million, and allocated USD 5.29 million to 11 projects, with an average grant size of USD 649,303, reflecting a 28% success rate. This funded research is focused mainly on gene transfer, environmental impacts, containment strategies, and advanced genetic technologies such as CRISPR, ensuring regulatory agencies have science-based data for risk assessment.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape for the genetically modified food market and feed continues to evolve, with a steady stream of applications being reported for import, processing, and commercialization. Key crops such as maize, soybean, cotton, and oilseed rape dominate submissions, reflecting their critical role in international food, feed, and industrial supply chains. There have been many recently concluded approvals and withdrawn applications, illustrating the rigorous oversight applied by authorities such as EFSA. Leading agricultural biotechnology companies, as Bayer CropScience, Syngenta, BASF, and Corteva Agriscience, remain at the forefront of innovation, which are efficiently driving the development of traits such as herbicide tolerance, insect resistance, and yield enhancement. Hence, such instances of regulatory activities indicate both the sustained market demand for GM crops and the careful balance between technological advancement and compliance with food safety standards.
GM Food and Feed Applications and Renewal Status by Intended Use: Food, Feed, Import, and Processing (2022-2025)
|
GMO |
Applicant |
Status |
Year |
|
Soybean FG72 |
Syngenta |
Ongoing |
2025 |
|
Soybean 305423 |
Corteva Agriscience |
Ongoing |
2024 |
|
Maize NK603 x T25 |
Bayer CropScience |
Ongoing |
2023 |
|
Cotton T304-40 |
BASF |
Concluded |
2025 |
|
Cotton GHB614 x LLCotton25 |
BASF |
Concluded |
2025 |
|
Maize T25 |
BASF |
Concluded |
2025 |
|
Maize MON 87427 |
Bayer CropScience |
Concluded |
2025 |
|
Maize NK603 |
Bayer CropScience |
Concluded |
2025 |
|
Maize MON 87460 |
Bayer CropScience |
Ongoing |
2023 |
|
Soybean MON 87708 |
Bayer CropScience |
Concluded |
2025 |
|
Soybean MON 87705 |
Bayer CropScience |
Ongoing |
2023 |
|
Soybean MON 87769 |
Bayer CropScience |
Ongoing |
2023 |
|
Cotton MON 531 |
Bayer CropScience |
Withdrawn |
2023 |
|
Cotton MON 531 x MON 1445 |
Bayer CropScience |
Withdrawn |
2023 |
|
Cotton MON 1445 |
Bayer CropScience |
Withdrawn |
2023 |
|
Cotton MON 15985 |
Bayer CropScience |
Withdrawn |
2023 |
|
Oilseed rape MON 88302 |
Bayer CropScience |
Concluded |
2025 |
|
Maize MON 89034 x 1507 x NK603 |
Bayer CropScience & Corteva Agriscience |
Concluded |
2024 |
|
Maize MON 810 |
Bayer Agriculture BV |
Concluded |
2024 |
|
Maize MON 89034 x 1507 x MON 88017 x 59122 |
Bayer CropScience & Corteva Agriscience |
Concluded |
2024 |
|
Oilseed rape GT73 |
Bayer Agriculture BV |
Concluded |
2022 |
|
Oilseed rape GT73 |
Bayer Agriculture BV |
Concluded |
2022 |
|
Maize MIR162 |
Syngenta |
Concluded |
2022 |
|
Oilseed rape MS8, Rf3 and MS8 x Rf3 |
BASF |
Concluded |
2023 |
|
Soybean 40-3-2 |
Bayer Agriculture BV |
Concluded |
2023 |
|
Soybean MON87701 x MON89788 |
Bayer Agriculture BV |
Concluded |
2023 |
|
Soybean MON87701 |
Bayer Agriculture BV |
Concluded |
2023 |
|
Soybean A5547-127 |
BASF |
Concluded |
2022 |
|
Cotton 281-24-236 x 3006-210-23 |
Dow Agrosciences |
Concluded |
2023 |
Source: Biosafety Advisory Council
Key Genetically Modified Food Market Insights Summary:
Regional Highlights:
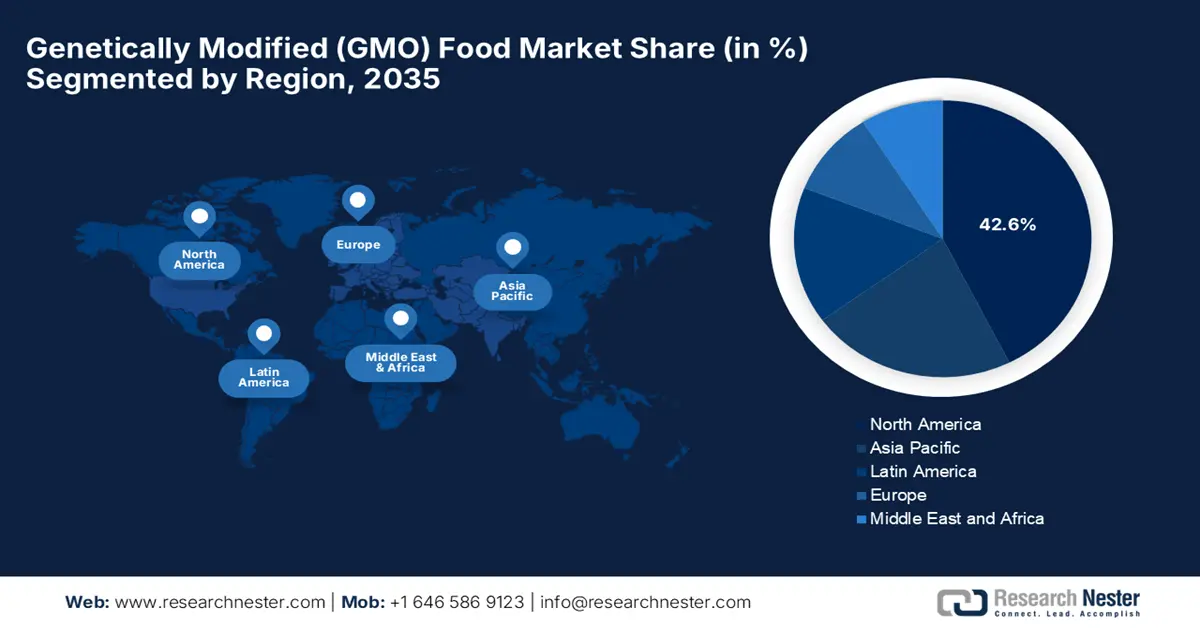
- North America is forecast to command a dominant 42.6% revenue share by 2035 in the genetically modified (GMO) food marke, reinforced by mature agri-biotechnology infrastructure, extensive regulatory clearances, and widespread commercialization of genetically engineered crops.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to emerge as the fastest-growing region through 2035, supported by rising food demand from rapid urbanization and population growth, alongside government-backed investments in biotechnology development and adoption.
Segment Insights:
- The maize segment is projected to capture a leading 38.6% share by 2035 in the genetically modified (GMO) food marke, attributed to its high-yield advantages and extensive utilization across food, feed, and biofuel value chains.
- The herbicide tolerance segment is expected to hold a substantial share by 2035, benefiting from its long-standing global adoption as a cost-efficient solution that simplifies weed management in large-scale crop cultivation.
Key Growth Trends:
- Rising global food demand
- Enhanced agricultural productivity
Major Challenges:
- Regulatory and approval complexities
- Public perception and consumer acceptance
Key Players: Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, Syngenta AG, BASF SE, DuPont, Pioneer Hi-Bred International.
Global Genetically Modified Food Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 123.9 billion
- 2026 Market Size: USD 133.6 billion
- Projected Market Size: USD 245.6 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 7.9% CAGR (2026-2035)
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: North America (42.6% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Asia Pacific
- Dominating Countries: United States, China, Brazil, Canada, Argentina
- Emerging Countries: India, Japan, Australia, South Korea, Mexico
Last updated on : 8 January, 2026
Genetically Modified (GMO) Food Market - Growth Drivers and Challenges
Growth Drivers
- Rising global food demand: This, along with food security needs, is one of the most important factors driving growth in the genetically modified food market. These foods help boost yields and ensure stable food supplies, especially in regions that are constantly facing food insecurity and climate stress. In this regard, in May 2024, Origin Agritech announced that it had received a GMO safety certificate for its variety called triple-stack transgenic maize BBL2-2, which combines two insect-resistance genes and one herbicide-tolerance gene, thereby marking a major milestone in terms of commercial deployment. This certification states that the maize meets strict safety standards and is expected to improve crop yields, pest management, as well as environmental sustainability. In addition, the company also reported strong progress in gene-editing innovations, which include a high-yield corn line representing more than 50% yield improvement.
- Enhanced agricultural productivity: The GM crops increase yield, pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, and climate resilience, thereby enabling farmers to produce more with less land and a very fewer inputs such as pesticides. As per an article published by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare in May 2025, India has become the first ever country in the world to develop genome-edited rice varieties such as DRR Rice 100 (Kamla) and Pusa DST Rice 1, which were developed by ICAR using CRISPR-Cas technology. These new rice varieties have promised higher yields, improved climate resilience, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and major savings in irrigation water, supporting both farmer prosperity as well as environmental sustainability. Hence, the country considers this as a major step toward food security and a second Green Revolution, denoting a positive genetically modified food market outlook.
- Advances in genetic engineering technologies: Evolution of modern techniques such as CRISPR and other gene-editing tools allows more precise, efficient development of improved crops. Therefore, these innovations are expanding the types of GM products and accelerating commercialization in the genetically modified food market. In this regard, Neocrop Technologies in August 2025 announced that it received regulatory clearance from Chile’s Agricultural and Livestock Service for the first CRISPR-edited wheat in the Americas, allowing it to proceed to field trials and commercialization under conventional crop regulations. It also notes that the wheat was developed using precision gene editing (CRISPR) to increase dietary fiber 5 to 10 times without introducing any type of foreign genes, addressing major nutrition gaps by also preserving baking quality.
Challenges
- Regulatory and approval complexities: One of the main challenges in the genetically modified food market is navigating through the complex and varying regulatory frameworks across countries. The approval processes for genetically modified crops and animals are mostly lengthy as well as costly, requiring extensive safety and environmental studies. Different nations have divergent standards, labeling requirements, and public reporting rules, which can ultimately cause delays to market entry and increase compliance costs, making it challenging for firms from price-sensitive regions. In addition, the aspect of regulatory uncertainty around emerging technologies such as CRISPR can create hesitation among developers and investors, slowing commercialization in this field.
- Public perception and consumer acceptance: The existence of consumer skepticism and negative perceptions of GMO foods remains yet another major burden for the expansion of the genetically modified food market. Most of the people around the world associate these genetically modified products with certain health risks, unnatural processes, or environmental concerns, even though scientific consensus supports their safety. Therefore, this misinformation can negatively influence purchasing decisions, which in turn leads retailers to limit GMO offerings. In addition to public protests, social media campaigns can also amplify resistance in this sector. The aspect of a very low consumer acceptance negatively affects GMO food market growth, as companies must balance innovation with marketing, education, and labeling strategies to build trust.
Genetically Modified (GMO) Food Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Year |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
7.9% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 123.9 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 245.6 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Genetically Modified (GMO) Food Market Segmentation:
Crop Type Segment Analysis
In the genetically modified food market the maize segment based on crop type is expected to garner the largest revenue share of 38.6% during the forecast period. The dominance of the segment is mainly propelled by the widespread adoption of GM maize for animal feed, high yield potential, and a heightened demand from food, feed, and biofuel industries. In December 2025, the European Commission reported that it had authorized the placing on the regional market of products containing or produced from genetically modified maize DAS-Ø1131-3, which was developed by Corteva Agriscience, following a favorable EFSA safety assessment confirming no risks to human or animal health or the environment. It also mentioned that this GM maize expresses glyphosate tolerance (DGT-28 EPSPS) and insect resistance (Cry1Da2) traits, supporting efficient pest control and crop management across food and feed uses. Therefore, such approvals solidify maize’s dominance in the GMO food market by enabling wider commercial use across the region.
Trait Segment Analysis
By the conclusion of 2035, the herbicide tolerance is anticipated to grow with a considerable share in the genetically modified food market. The subtype is considered to be the most widely planted genetic modification across the globe since it simplifies weed control and reduces labor and input costs. HT crops such as soybeans, corn, and canola dominate commercial GMO cultivation and have been widely adopted in primary producing countries for decades. As per the article published by USDA in July 2024, genetically engineered seeds were first commercially introduced for major field crops in the U.S. over two decades ago, and their adoption expanded rapidly in subsequent years. It also mentioned that the most widely planted genetically engineered traits are herbicide tolerance and insect resistance, which can be used individually or combined as stacked traits in a single seed. According to the USDA’s Economic Research Service, these technologies have become central to modern U.S. agriculture, improving crop protection and farm productivity, hence denoting a wider segment scope.
Application Segment Analysis
In the application segment, animal feed is predicted to capture a significant share of the genetically modified food market over the discussed timeframe. The major portion of GMO crop production goes into animal feed, particularly soybean meal and corn, which in turn is driven by global livestock and poultry demand. In addition, the livestock feed costs represent a large share of production expenses, wherein the GMO inputs provide consistent quality and cost advantages, making the animal feed segment a leading revenue contributor in this field. Moreover, the adoption of GM crops in animal feed helps improve feed efficiency and nutrient absorption, supporting higher productivity in livestock and poultry. Regulatory approvals for GM soy and corn in major markets such as the U.S., Brazil, and the EU are also enabling large-scale integration into feed supply chains. Furthermore, the heightened demand for meat, dairy, and poultry products across the globe continues to drive the sustained growth of the animal feed segment within the market.
Our in-depth analysis of the genetically modified food market includes the following segments:
|
Segment |
Subsegments |
|
Crop Type |
|
|
Trait |
|
|
Application |
|
|
Product Type |
|
|
Modification Technique |
|
|
End use |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Genetically Modified (GMO) Food Market - Regional Analysis
North America Market Insights
North America genetically modified food market is likely to maintain leadership, contributing to the largest 42.6% revenues by the end of 2035. The well-established agricultural biotechnology infrastructure, widespread regulatory approvals, and high adoption rates of genetically engineered crops are the key factors fueling the region’s leadership. As of the September 2024 data from the U.S. FDA, the common GMO crops include soybeans, corn, cotton, canola, sugar beets, alfalfa, papaya, potatoes, apples, and summer squash, with soybeans, corn, and cotton making up the majority of their respective plantings. Most GMO crops in the U.S. are used for animal feed or processed into ingredients such as oils, cereals, and snack foods, rather than appearing directly as fruits or vegetables in grocery stores. Further, the region also benefits from advanced seed R&D programs and integration of precision farming technologies, which promote continual trait innovation in commercial crops.
The presence of major biotech companies and universities are allowing crops with enhanced traits such as stress tolerance, optimized nutrient profiles, and reduced environmental inputs, driving business in the U.S. genetically modified food market. According to the article published by the U.S. Department of Agriculture in December 2025, the country has been witnessing 90% of corn, upland cotton, and soybean acres now planted with GE varieties. It also mentioned that by the conclusion of 2025, adoption of HT seeds reached 96% for soybeans, 93% for cotton, and 92% for corn, whereas the Bt traits covered 87% of corn and 91% of cotton acres, with stacked varieties increasingly dominating U.S. crop production. Furthermore, the regulatory framework supports streamlined evaluation and commercialization pathways that encourage both domestic deployment and export of GMO products, contributing to overall GMO food market growth.
Canada genetically modified food market is growing on account of a trait-based regulatory approach, which evaluates products on their characteristics rather than the development method. This policy has enabled the approval of markets for gene-edited crops along with traditional GM varieties, fostering a product pipeline of improved crops and increasing opportunities for farmers in the country. In this context, the GM Watch 2025 article reported that the country’s grocery stores sell only three genetically engineered fruits and vegetables: GM sweet corn, GM papaya, and a GM pink-fleshed pineapple, though these products are not widely available. It also mentioned that the federal government has begun exempting many new gene-edited foods from regulation, meaning most will reach the market without Health Canada's mandatory notification to consumers. Hence, such instances are driving market growth by expanding consumer options and increasing the adoption of biotech crops in fresh produce.
APAC Market Insights
The Asia Pacific genetically modified food market is considered to be the fastest growing, fueled by the expanding populations and rapid urbanization, which are elevating demand for efficient and sustainable food production systems. Governments and agricultural agencies across the region are making investments in biotechnology research, public–private partnerships, and capacity building to support the development and adoption of GMO crops. In July 2024, Japan’s Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (MAFF) confirmed that regular surveys of GM crop sites, which include rapeseed, soybean, corn, and cotton, showed no cross-contamination with nearby non-GM crops. Also, the aspect of strict protocols and continuous monitoring ensures that GM crops do not affect local biodiversity, addressing public concerns about accidental spillage. Hence, such instances of official assurance support consumer confidence and the safe adoption of GM crops in Japan’s agricultural sector.
The strategic focus on food security and self-sufficiency, regulatory authorities advancing biosafety evaluations for multiple genetically engineered crops, are the major driving factors for the China genetically modified food market. Simultaneously, the domestic biotech firms, often in collaboration with public research institutes, are accelerating the development of improved varieties to reduce reliance on imports. In this regard, Origin Agritech Ltd. in June 2025 reported that it advanced its biotechnology capabilities, which include progress on GMO corn hybrids, the BBL2-2 trait certification, the launch of the MIGC 20K gene chip, and partnerships with 12 major agricultural companies to drive smart corn breeding and gene editing initiatives. Origin also mentioned that it strengthened market presence through strategic collaborations, field demonstrations of around 300 corn varieties, and the development of R&D platforms in multiple provinces, positioning itself for long-term growth in the country’s market.
India genetically modified food market is backed by ongoing policy debates and regulatory reviews, particularly relating to genetically modified crops for food and feed. The country’s market also benefits from investments in genome editing research, capacity building, and state-led trials with a prime focus to align biotechnological innovation with local agronomic needs. In this regard, the country’s GM Info in May 2025 revealed that the coalition for a GM-Free India has demanded the immediate withdrawal of two recently released, untested gene-edited rice varieties, Kamala (DRR Dhan 100) and Pusa DST Rice 1, arguing that their release violates the law in the country, bypasses rigorous safety testing, and threatens environmental sustainability. The Coalition warns that SDN-1 and SDN-2 gene-editing techniques used to develop these varieties are imprecise, can create unintended genetic changes, potentially introduce foreign DNA, and pose risks of toxicity and loss of rice biodiversity. Therefore, releasing gene-edited rice varieties has the complete potential to drive GMO food market growth by promising higher yields that attract farmers and boost agricultural productivity.
Europe Market Insights
Europe genetically modified food market is progressing at a notable pace since it is governed by stringent regulatory frameworks that emphasize rigorous safety assessments and traceability. The continued imports and use in food and feed continue under strict oversight, fostering monitoring systems that inform policy decisions and consumer choice throughout the region. In December 2025, SOS reported that a qualified majority of EU Member States backed the deregulation of genetically modified plants produced using new genomic techniques, exempting them from risk assessments, labeling, and traceability requirements, but in turn allowing full patenting. In addition, the critics, including Save Our Seeds, state that this move favors biotech corporations rather than farmers, wherein such instances reduce the compliance costs, speeding up product commercialization, and encouraging more investment in biotech crop development.
The cautious regulatory implementation and active public engagement are the major driving factors for the Germany genetically modified food market. Research institutions conduct gene editing and trait development projects with a focus on sustainability and environmental impact, whereas policymakers balance innovation with precautionary risk assessments. In July 2025, the European Commission announced that it had approved a new genetically modified soybean for use in food and feed, which was followed by a scientific review and recommendation by the region’s food safety authority. It also mentioned that in Germany, as in other EU countries, the approval does not allow cultivation, and all products derived from this soybean must comply with strict labelling and traceability requirements. In addition, the authorization is valid for 10 years and ensures there is no risk to human or animal health or the environment, hence making it suitable for standard GMO food market growth.
The U.K. has redefined its regulatory framework to support innovation in genetic technologies, including gene editing. This updated landscape facilitates the development and approval of GMO and gene-edited crops that can support sustainable production in the U.K. genetically modified food market. In March 2023, the UK government reported that it had passed the Genetic Technology (Precision Breeding) Act, which deliberately enables the use of gene editing to develop crops and animals with traits, such as drought and disease resistance, while also maintaining strict GMO regulations. It also mentioned that this act introduces a science-based regulatory system to support research, innovation, and commercialization of precision-bred plants, with plans for animals, enhancing food security and climate resilience. Hence, this legislation positions the country as a predominant leader in agri-food innovation, thereby helping farmers produce even healthier, more resilient, and sustainable food.
Key Genetically Modified (GMO) Food Market Players:
- Bayer AG (Germany)
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- Corteva Agriscience (U.S.)
- Syngenta AG (China/Switzerland)
- BASF SE (Germany)
- DuPont (U.S.)
- Pioneer Hi-Bred International (U.S.)
- Seminis (U.S.)
- Groupe Limagrain (France)
- KWS SAAT SE (Germany)
- Mahyco (Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Co.) (India)
- Sakata Seed Corporation (Japan)
- DLF Seeds & Science (Denmark)
- Stine Seed Company (U.S.)
- Inari Agriculture (U.S.)
- Bayer AG is one of the leading global life sciences companies, which has a strong presence in agricultural biotechnology. The firm’s division develops genetically modified seeds for corn, soybean, cotton, and vegetables by integrating traits such as herbicide tolerance, pest resistance, and drought resilience. Bayer AG is also focused on sustainability, digital agriculture, and precision breeding, with a prime focus on supporting farmers with high-yield solutions.
- Corteva Agriscience is formed from DowDuPont’s agriculture division and is a major US-based GMO seed and crop protection company. The company specializes in corn, soybean, and cotton genetically modified varieties by combining high-yield traits with stress tolerance and pest resistance. In addition, Corteva makes investments in R&D, digital agriculture platforms, and biotechnology innovation, which includes advanced gene-editing research.
- Syngenta AG is a central player in this field and is a global agribusiness leader in crop protection and genetically modified seeds. The firm is pursuing continued growth through acquisitions, licensing agreements, and considerable R&D programs by integrating biotechnology innovations with digital agriculture solutions. Furthermore, Syngenta has a strong presence in both China and Switzerland, which allows it to balance international expansion with regional expertise, making it one of the most influential players in this GMO food market.
- BASF SE is operating through a robust agricultural solutions division that is focused on GMO crops and biotech seed innovation. The company also develops genetically modified corn, cotton, and specialty crops featuring herbicide tolerance, insect resistance, as well as stress-adaptive traits. In addition, BASF makes continued investments in gene-editing technologies, biotechnology R&D, and precision agriculture tools to maintain competitiveness.
- DuPont is currently integrated with Corteva Agriscience for its national and international agriculture operations. Besides, the company has been a pioneer in transgenic trait development, insect-resistant Bt crops, and herbicide-tolerant varieties. Furthermore, DuPont emphasizes continued innovation through biotechnology research, strategic licensing, and global partnerships, collaborating with academic institutions and seed companies to enhance its GMO portfolio.
Below is the list of some prominent players operating in the global genetically modified food market:
The genetically modified food market is dominated by long-established giants and innovative biotech firms. Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, Syngenta AG, BASF SE, and DuPont are the most influential players that are driving international genetic trait development in this GMO food market. Besides, these companies leverage continued R&D investments, partnerships, and integrated seed‑trait portfolios to secure their market positions. In this regard, in November 2025, Syngenta reported that its REVERTE program has been recognized as best-in-class for efficiently transforming agriculture by restoring degraded pasturelands and promoting regenerative practices in Brazil, which benefits 280,000 hectares across 11 states. In addition, Syngenta also mentioned that it aims to expand REVERTE to recover 1 million hectares by the end of 2030, which demonstrates its commitment to climate-smart solutions within the global GMO sector.
Corporate Landscape of the Genetically Modified Food Market:
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, GDM announced an agreement to acquire 100% of AgReliant Genetics, uniting GDM’s global leadership in soybean genetics with AgReliant’s strong corn breeding and research capabilities to strengthen its high-performance seed portfolio, expand the firm’s footprint across corn and soybean genetics.
- In January 2025, Origin Agritech announced partnerships with 12 leading agricultural companies focusing on transgenic varieties, gene editing, and molecular breeding. The company showcased its MIGC 20K gene chip, enabling variety development, transgenic identification, and breeding efficiency, thereby accelerating GMO seed innovation and commercialization.
- Report ID: 117
- Published Date: Jan 08, 2026
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Genetically Modified Food Market Report Scope
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




