Posted Date : 15 October 2025
Posted by : Shweta Singh
The world of investing is undergoing a significant transformation. Amid growing concerns about climate change, inequality, and corporate responsibility, Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria have taken center stage. These three pillars are increasingly influencing how businesses function and how investors evaluate performance, not just in terms of profit, but in terms of purpose and long-term resilience. This blog takes a closer look at what ESG symbolizes, why it is gaining traction across industries, and how companies and investors can benefit from sustainable strategies. Along with this, we will also learn about key statistics, global trends, and real-world examples that show how ESG is defining the future outlook of finance.
Why ESG Matters in Today's World
The rise of ESG reflects a growing awareness of sustainability and ethical responsibility. Here is why ESG is important:
- Addressing Climate Change: The environmental factor of ESG is important as the world struggles with climate change. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) warns that global temperatures could rise by 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels by 2030 without any prompt action. Companies embracing ESG practices, such as reducing carbon footprints or moving to renewable energy, contribute to removing climate risks. For instance, a 2024 Bloomberg report noted that global renewable energy capacity rose by 10% in 2023, due to ESG-focused investments.
- Aligning with Stakeholder Demands: Consumers, employees, and investors are increasingly wanting ethical practices. A 2023 survey disclosed that 78% of global consumers choose brands with credible sustainability practices. Similarly, employees also target workplaces with inclusive and fair policies along with social responsibility. ESG helps companies to fulfill their demands, enhance brand reputation, and customer engagement.
- Changing Regulatory Landscape: Governments are implementing stringent rules for more transparent and credible results. The Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) in the EU, applicable from 2021, and the SEC’s climate-related rules of 2022 require companies to report on greenhouse gas pollution. Thus, compliance with such strict regulations is now a business imperative. Businesses that stay ahead of these changes are better positioned to attract investment and avoid penalties.
- Proven Financial Benefits: Strong ESG performance is increasingly noted as a marker of financial health. A 2023 MSCI analysis found that firms with high ESG ratings had an annual stock return advantage of 7.4% over their peers. These companies often face fewer legal risks, have more engaged employees, and adapt better to any disruption.
The Components of ESG in Detail
1. Environmental: Driving Sustainable Operations
This pillar focuses on how a company minimizes its ecological impact. The key metrics comprise:
- Emissions Tracking: Calculating direct (Scope 1), indirect (Scope 2), and supply chain (Scope 3) emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizing energy use by eliminating waste.
- Waste and Resource Management: Reducing waste and promoting recycling, or circular economy practices.
For instance, Microsoft committed to being carbon-neutral by 2030, investing $1 billion in the Climate Innovation Fund. Such initiatives not only lower environmental impact but also bring on ESG-focused investors.
2. Social: People Centric Practices
Social considerations relate to employee well-being, ethical labor practices, diversity, and community involvement.
- Employee Support: Mental health programs, safety measures, and fair compensation in industries are increasingly being encouraged to be non-negotiable.
- Community Engagement: From ethical and responsible sourcing to philanthropic initiatives, brands are anticipated to make a meaningful contribution to society. For instance, outdoor apparel company Patagonia allocated 1% of its annual revenue to environmental nonprofits and employs strict labor rules across its supply chain.
3. Governance: Leading with Integrity
Good governance assures ethical leadership and transparency in decision-making. The key factors include:
- Board Composition: Diverse boards reduce the likelihood of oversight scandals. A 2024 study from Harvard Business Review found that such companies are 20% less likely to face governance-related issues.
- Anti-Corruption Policies: Enforcing measures to prevent fraud and bribery.
- Clear Reporting: Offering transparent, precise financial and ESG reporting.
For instance, Unilever is often known for its strong governance structure, and its consistent ranking in ESG indices like the Dow Jones Sustainability Index reflects that commitment.
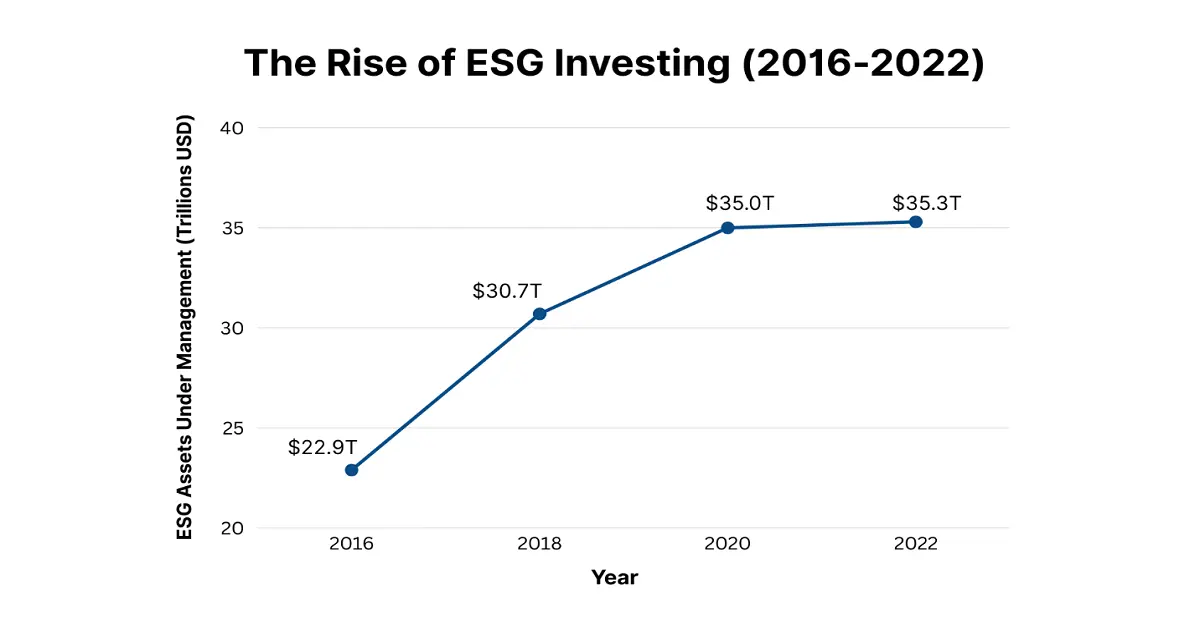
The Rise of ESG Investing
ESG investing has grown from a niche approach to a global movement. According to the Global Sustainable Investment Alliance, ESG assets under management hit $35.4 trillion in 2022, accounting for about one-third of all managed assets globally. This growth is powered by several factors, as mentioned below:
- Institutional Investors: Pension funds and asset managers, such as BlackRock, are focusing on ESG. In 2023, BlackRock unveiled that 60% of its new investments met ESG criteria.
- Retail Investors: Millennials and Gen Z are at the forefront, encouraging ESG-aligned portfolios. A 2024 survey revealed that 85% of individual investors consider ESG factors while investing.
- Strong Returns: ESG funds have shown high resilience during market volatility. During the 2020 market crash, ESG funds outperformed traditional funds by 4.3%, according to our analysis.
The Future of ESG
The future of ESG is changing, and a few trends are likely to shape the future as mentioned as follows:
- Stricter Rules: Governments will likely enforce stricter ESG reporting, with the EU leading the way through initiatives like the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD).
- Smarter Tools: AI and blockchain will improve ESG data accuracy and transparency. For instance, blockchain can track supply chain sustainability in real-time.
- Social Justice in Focus: Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) are expected to become more central to ESG assessments.
- Net-Zero Commitments: In 2024, over 4,000 companies globally had promised net-zero emissions by 2050, as per the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi).
Contact Us







