Posted Date : 17 September 2025
Posted by : Akshay Pardeshi
In recent years, blockchain has rapidly transformed from a niche concept powering cryptocurrencies into a cutting-edge technology set to transform sectors ranging from finance, healthcare, to logistics, and the entertainment industry. But what exactly is blockchain, and why is it being acclaimed as a foundational component of the digital economy? In this blog, we will discover blockchain technology, see how it works, analyze its advantages, and step into real-world applications, building the next era of digital transactions, data management, and trust.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records transactions across a network of computers in a safe, transparent, and immutable manner. Unlike a conventional centralized database handled by an individual authority, blockchain assures that no single party controls the data, making it resistant to tampering, fraud, or censorship.
The blockchain market is rapidly evolving with the rising tokenization of real-world assets, high adoption of blockchain technology by financial institutions, and rising demand for decentralized finance (DeFi). As of 2025, the global blockchain market is predicted to reach $95.2 billion, registering a CAGR of over 66.5% from 2024 to 2035. Moreover, over 80% of top global companies, including IBM, Microsoft, and JPMorgan, are actively exploring or using blockchain solutions.
Blockchain now supports over 25,000 cryptocurrencies, and more than 200 million blockchain wallets worldwide. Its applications are not just limited to finance, as in the enterprise domain, more than 70% of supply chain leaders aim to apply blockchain technology to improve transparency and efficiency. In the healthcare industry, blockchain adoption is rising, with the industry anticipated to surpass $10 billion by 2030, due to its potential in securing medical records and optimizing interoperability. These figures highlight the increasing adoption of technology and its foundational role in the digital transformation of industries.
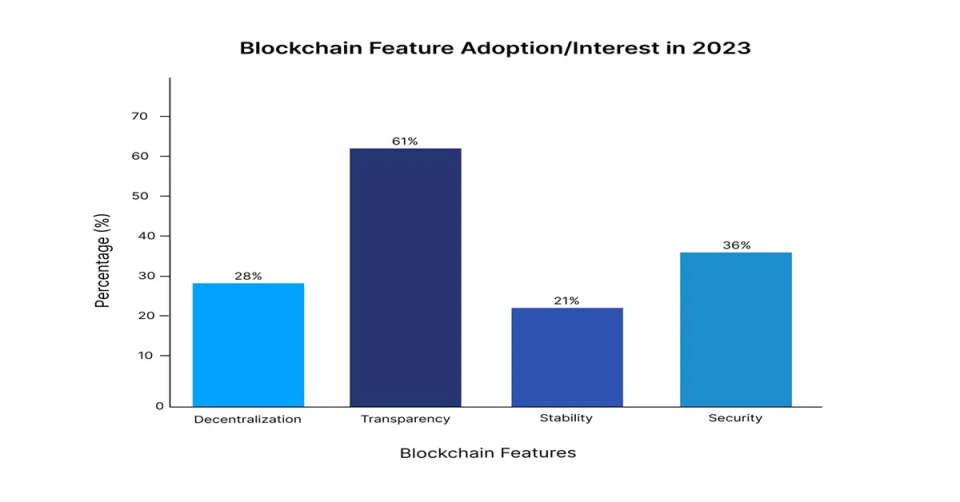
Characteristics of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralization: Instead of depending on a central server or authority, blockchain allocates control across a peer-to-peer (P2P) network. Each participant (or node) in the network holds a copy of the ledger, and consensus algorithms are used to validate transactions.
- Transparent process: Transactions captured on a public blockchain are open to all network participants. This level of clarity increases trust and decreases the need for intermediaries.
- Stability: Once a transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain, it cannot be deleted or changed. This provides an impeccable record of data and activities.
- Security: Blockchain utilizes modern cryptographic techniques to safeguard transactions and user identities. Any attempt to change data would require the consent of the majority of the network, an almost impossible feat for large, decentralized systems.
Below is a graph focusing on the adoption or impact of these blockchain features, with each bar representing the percentage of adoption or interest in 2023.
Applications of Blockchain
|
Application Area |
Description |
Industry Examples |
|
Cryptocurrencies |
Secure and decentralized digital currencies use blockchain to record transactions. |
Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin |
|
Supply Chain Management |
Enhances transparency, traceability, and efficiency by recording the product journey on the blockchain. |
IBM Food Trust, VeChain |
|
Smart Contracts |
Self-executing contracts with terms written into code that run on blockchain platforms. |
Ethereum, Hyperledger |
|
Voting Systems |
Enables secure, tamper-proof digital voting with transparent and verifiable results. |
Voatz, Follow My Vote |
|
Healthcare |
Stores and shares medical records securely, ensuring data integrity and patient privacy. |
Medicalchain, BurstIQ |
|
Identity Management |
Provides secure, decentralized digital identities, reducing fraud and identity theft. |
Sovrin, uPort |
|
Real Estate |
Facilitates transparent property transactions and land registry on immutable ledgers. |
Propy, Ubitquity |
|
Banking & Finance |
Improves cross-border payments, reduces fraud, and streamlines clearing and settlement processes. |
Ripple, JPM Coin |
|
Intellectual Property |
Protects copyrights, patents, and digital content ownership via timestamped blockchain records. |
Ascribe, Po.et |
|
Energy Trading |
Enables peer-to-peer energy trading and decentralized grid systems. |
Power Ledger, WePower |
The Future of Blockchain
As blockchain technology progresses, it is becoming a critical factor for a decentralized digital future. What was once considered a niche innovation linked to cryptocurrency has now transformed into a foundational layer for creating new digital ecosystems. Given below are some of the most significant ways in which blockchain is set to reshape the technological landscape in the coming years:
1. Web3 and the Rise of a User-Centric Internet: Web3 is designed to overturn the current internet model dominated by centralized corporations and instead create a digital space where users own their data, control their online identities, and directly interact with services without depending on intermediaries. Blockchain technology enables this shift by providing the infrastructure for decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and self-sovereign identity systems. Platforms such as IPFS for decentralized file storage and Ethereum for smart contract execution are just the beginning. In this new paradigm, power is redistributed from tech giants to individuals, encouraging a more equitable, private, and censorship-resistant internet.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi showcases one of the most transformative uses of blockchain, creating an open, transparent, and permissionless financial system. Using smart contracts on public blockchains such as Ethereum, DeFi platforms offer borrowing, lending, trading, and yield farming services, all without traditional banks or financial intermediaries.
Protocols like Uniswap (decentralized exchange), Aave (lending/borrowing), and Compound (interest-earning deposits) have collectively captured over $100 billion in digital assets, highlighting the substantial growth and real-world utility of DeFi. This decentralized infrastructure not only improves accessibility and efficiency but also encourages financial inclusion by allowing anyone with an internet connection to participate. Looking forward, as scalability solutions like Layer 2 networks (e.g., Arbitrum, Optimism) and Ethereum 2.0 evolve, DeFi is expected to become faster, cheaper, and more robust, poised to challenge and complement traditional finance at scale.
3. NFTs and the Reinvention of Digital Ownership: Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have introduced a whole new method to define and trade ownership in the fast-growing digital world. Built on blockchain, NFTs represent unique, indivisible digital assets, whether they are art, music, collectibles, in-game items, virtual real estate, or even event tickets.
What sets NFTs aside is their authentication and scarcity. Each NFT has a unique identifier recorded on the blockchain, proving authenticity and origin. Platforms such as OpenSea, Rarible, and Foundation have emerged as marketplaces for digital creators and collectors, allowing a creator economy where artists can monetize their work directly and earn royalties on secondary sales. Beyond the arts, NFTs are rapidly expanding into real estate, identity verification, academic credentials, and supply chain management, offering new regulations for verifying ownership and provenance across sectors.
4. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Digitizing National Economies Governments around the globe are exploring the concept of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), state-issued digital currencies built on blockchain or distributed ledger technologies. Unlike decentralized cryptocurrencies, CBDCs are managed by central agencies but benefit from the efficiency and traceability that blockchain offers. CBDCs aim to modernize monetary systems by permitting instant cross-border payments, reducing transaction costs, enhancing financial inclusion, and increasing transparency in financial activities. While the implementation of CBDCs raises concerns around surveillance and privacy, they are undeniably a strong step toward mainstream blockchain adoption at the state level.
5. Blockchain Interoperability: One of the primary hurdles faced by the blockchain industry is fragmentation. With thousands of blockchains operating independently, each with its own standards, protocols, and assets, there is a rising need for interoperability. Smooth communication between different blockchain networks is important for unlocking the full potential of decentralized technologies. Projects such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and Chainlink are leading the way to establish frameworks that allow blockchains to interact, share data, and move assets across networks securely. This interoperability is necessary for forming complex decentralized ecosystems where decentralized finance, gaming, supply chains, and identity systems can work in harmony. As these solutions advance, we will see more fluid, collaborative environments that function more like the internet itself.
Blockchain: A Revolution in Progress
Blockchain is far more than a passing trend; it is a technological revolution that is steadily reframing the architecture of our digital world. Its potential extends across industries and geographies, transforming how we handle finance, identity, ownership, governance, and trust. Yet, this promising future is not without hurdles. Issues such as flexibility concerns, energy consumption, regulatory ambiguity, and user adoption must be managed for blockchain to reach its full capability. The good news? Solutions are actively being developed, with innovation in areas like Layer 2 scaling, Proof-of-Stake consensus, regtech, and user-friendly wallets making blockchain more accessible and sustainable every day.
Contact Us







