Posted Date : 05 October 2024
Posted by : Parul Atri
The use of advanced manufacturing technology has the ability to alter manufacturing procedures and open up new business prospects. However, advanced manufacturing is unlikely to entirely substitute existing technologies in the near future.
One reason for this is the fact that numerous existing technologies, particularly for smaller-scale operations, remain effective and efficient. Additionally, some businesses, especially smaller ones, may find it prohibitively expensive to purchase and maintain the tools and software required for advanced manufacturing.
Additionally, the shift to advanced manufacturing technologies necessitates a sizable investment in education and training to create the necessary skills for workers to use and maintain these technologies. Hence, this factor refrains particularly the small organization to skill their workers in order to handle advanced manufacturing owing to lack of investment.
Manufacturing is the root of all technological innovations and developments. Any improvements in manufacturing often drive the growth of other innumerable industries and businesses farther down the supply chain. Utilizing cutting-edge technology and processes to increase manufacturing industries' competitiveness is known as advanced manufacturing. Advanced manufacturing uses flexible production techniques that make the most of capital equipment and are more effective, efficient, and quick to respond. Although there are some situations where traditional, specialized methods are still appropriate, like with long, predictable production runs, advanced manufacturing has the ability to handle the various production requirements and mass customization that industries frequently face, without the need for a lot of capital investment.
Advanced manufacturing technologies enhance productivity by giving manufacturers the ability to scale up or down based on market needs and demands. In order to integrate manufacturing and commercial activities into a continuous, effective operation, advanced manufacturing relies on information and communication technology (ICT). This includes all areas of the value chain, from ideation to end-of-life considerations. In order to keep manufacturing at the forefront, advanced manufacturing technologies, often known as "Smart Manufacturing," are crucial.
Advantages of Advanced
Manufacturing Techniques
- When manufacturing operations are more automated and economical, resources may be concentrated more on research and development, enabling the introduction of novel and exciting products.
- Modern production techniques are more accurate, consistent, and efficient overall, which results in higher-quality products that are more dependable, accessible, and reasonably priced.
- By automating manufacturing activities, advanced manufacturing helps with leaner production efforts so that staff can concentrate on more creative work.
- Better market responsiveness is made possible by advanced manufacturing's flexibility and optimized planning and scheduling.
The Future Scope for Market for
Advanced Manufacturing
The size of the world market for advanced manufacturing is anticipated to reach about USD 78 billion in 2035 with a CAGR of ~22% during the forecast period 2023-2035. Technology developments and the rising popularity of new applications can be used to explain the rapid market revenue growth of advanced manufacturing. Players in the advanced manufacturing industry have a lot of opportunities to improve their production capacity and efficiency thanks to the development of new methods, materials, and equipment.
Advanced Manufacturing's Goals
Gaining a competitive edge in the market is the goal of advanced manufacturing, and it accomplishes this in various ways. Increasing output is undoubtedly one of the primary goals of sophisticated manufacturing. More can be sold as you produce more. This does not imply that increased production is the only goal of modern manufacturing. Other areas such as process optimization and efficiencies can be improved as well. For instance, advanced manufacturing aims to shorten the time it takes to develop a product, as well as lower unit costs, material content, material inventories, and the amount of underutilized capital equipment.

Types of Advanced Manufacturing
- Efficient Production: Simultaneous engineering, as opposed to sequential engineering, is the focus of this work, which also includes design, simulation, physical and computer modeling, cutting-edge manufacturing technology, and control methods. Precision casting and quick prototyping both employ this.
- Intelligent Production: Employs methods for the increased lifespan and best utilization of manufacturing facilities using ICT and related logistical systems. This is accomplished by effective monitoring, routine upkeep, and repairs.
- Effective Organization: Coordinating and taking advantage of industrial resources, both tangible and intellectual. This is applied to virtual tendering, businesses, shared resources and facilities, innovative organizational structures, incubation units, knowledge management, trade, and online commerce.
Advanced Manufacturing Solutions
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning AI and machine learning can bring about a total transformation of manufacturing. Even though AI has been around for quite some time now, the latest developments such as cloud computing, big data, and machine learning are driving the concept to the forefront of the world economy. AI in manufacturing can be optimized to facilitate real-time data-driven solutions by collecting data from different branches of a business. For example, data from the production line can help calculate and predict manufacturing cycle time and enable accurate planning and scheduling. Using sensors, AI can monitor the quality of the products or the condition of the production equipment. AI can be used in procurement to make accurate demand forecasts and order necessary raw materials accordingly. It has been predicted that AI is capable of driving a 40% increase in profits in the manufacturing industry by the year 2035.
- Nanotechnology: The need for smaller components grows as our devices get smaller. As designers need to pack more functionality into a compact design structure, nanotechnology is increasingly at the forefront of several sectors. Additionally, nanoscale particles are used in chemical and biological applications where they can improve material characteristics, regulate light spectroscopy, and modify chemical reactivity.
- Robotics: Robotics makes the list of modern manufacturing processes, which should come as no surprise given that these automated technologies enable heavy lifting, precise movement & joining, and improved work uniformity across numerous production units. Industrial robotics is incredibly useful to perform dangerous operations as it reduces stakeholder risk, overhead, and waste while producing goods more reliably, quickly, and affordably. Automotive, aerospace, forging, consumer goods, and many other industries use robots often, and as our understanding of robotics advances, so does our capacity to introduce automated systems into other fields.
- Additive Manufacturing: CAD software or 3D object scanners are used in additive manufacturing to instruct machines to deposit material in exact geometric shapes layer by layer. By doing this, manufacturers decrease the likelihood that a system would fail, which has numerous advantages such as lowering weight, complexity, and thermal dissipation issues. Aerospace, medical, prototype, automotive, consumer products, and many more sectors benefit from additive manufacturing, and these industries will expand as the technology becomes more affordable and simpler to use.
- Laser machining: Laser machining and welding, which use laser technology, enable the quick and high-precision production of items. Lasers eliminate cracking and poor joining while maintaining the integrity of the part by precisely controlling the amount of heat that is sent into the material. Pressure vessels, proximity sensor welding, battery welding, sensitive electronics, and many more goods are currently made safer and more precisely using these technologies.
Industries Utilizing
Advanced Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing can’t be incorporated into just about any company that can pay for composite materials or cloud computing. It can succeed only if there is a sophisticated IT infrastructure in place, such as in electric vehicle, robotics, aerospace, and some other industries.
List of industries being transformed by advanced manufacturing techniques today:
- Consumer Products: Early in the product development life cycle, 3D printing is excellent for creating intricate consumer electronics with realistic aesthetics and functionality. Early iterations that were rapidly and precisely provided have been beneficial for sporting products. Detailed architectural models and entertainment props and costumes are some more examples of successful usage. More consumer products might switch to additive manufacturing in the coming years as 3D printing technology improves build volume and speed.
- Energy: The capacity to quickly create specialized, mission-critical components that can survive harsh conditions is crucial for success in the energy business. The development of efficient, lightweight, on-demand components and ecologically-friendly materials using additive manufacturing offers solutions for various requirements and field functions.
- Medical: Solutions for additive manufacturing are being used by the quickly evolving medical sector to bring innovations to practitioners, patients, and research facilities. Medical producers are using a variety of hard, flexible, opaque, and transparent 3D printing materials to create designs that are more customizable than ever before. Through the use of surgical grade components, functional prototypes, realistic anatomical models, and functional prototypes, advanced manufacturing is enabling previously unimaginable developments for life-saving technologies. Orthopedic biomaterial implant devices, dental devices, pre-surgery models from CT scans, custom saw and drill guides, enclosures, and customized instruments are a few applications reshaping the medical sector.
Latest Innovations in
Advanced Manufacturing
- Simulation: The second-most popular innovation and management science employed by manufacturing managers is the process of simulation. Just-in-time manufacturing is supported by simulation, which has the following advantages: computation of the ideal resources needed, time spent in the system by parts, time spent during transit, and utilization of machines and personnel. Using Integrated Computational Materials Engineering (ICME), product engineers can design a virtual product model and test out its performance in different conditions before proceeding with real-life production. Virtual manufacturing can simulate manufacturing processes, which is very helpful to remove inefficiencies and streamline production.
- Augmented Reality: For shop floor technicians, augmented reality delivers an immersive, detailed instruction manual. The interior workings of machines are shown for employees to learn from, which will improve the educational experience and reduce wasteful expenditures of time and money. Augmented reality can aid in performing maintenance for the production equipment. Since AR applications combine actual and virtual reality in an innovative way, they can help manufacturers optimize the production process. It promotes the correctness and assessment of digital planning in a physical setting.
Future of Advanced Manufacturing
Cobots, or collaborative robots, are made to undertake laborious or hazardous activities alongside humans. It is anticipated that as cobot technology develops, they would be utilized more frequently in manufacturing, increasing productivity and safety. Moreover, a production strategy known as circular manufacturing prioritizes reducing waste and increasing resource efficiency. Using renewable energy sources during production and creating items that are easily disassembled and recyclable are two aspects of this strategy.
How small organizations can boost the adoption of advanced manufacturing?
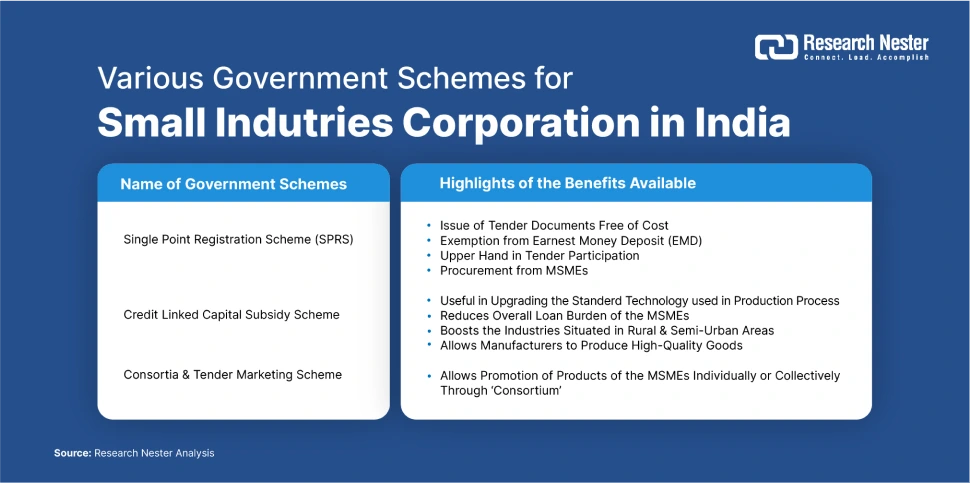
To develop knowledge and experience in advanced manufacturing, small enterprises can collaborate with specialists like consultants, consultants, and technology providers. This can assist them in overcoming technical difficulties, staying current with current events, and having access to resources like money and training. Additionally, small enterprises can take use of government assistance initiatives including grants, loans, and tax breaks to help finance the adoption of sophisticated manufacturing equipment. By making technology more affordable for small firms, these programs can assist to lessen the financial strain of investing in it.
In Conclusion
Advanced manufacturing is not just another passing trend or a buzzword that will soon be forgotten in a few years. It is a phenomenon that will grow rapidly in the near future, paving the way for remotely managed smart factories that deploy new and advanced manufacturing technologies. The first step in this direction would be for manufacturers to begin establishing an infrastructure for their advanced manufacturing initiatives to take flight.

Contact Us







